May 17, 2017 – Clinical trial results from a first-in-human study evaluating the acute feasibility of an investigational radiofrequency (RF) balloon catheter in treating patients with atrial fibrillation (AF or AFib) found the device could uniformly achieve pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) in all patients without the need for "touch-up" with a focal ablation catheter. Data from the RADIANCE study was presented for the first time during a late-breaking clinical trial session at Heart Rhythm 2017, the Heart Rhythm Society’s 38th Annual Scientific Sessions.
The “PV Isolation with a Novel Multi-electrode Radiofrequency Balloon Catheter that Allows Directionally-Tailored Energy Delivery (RADIANCE)” study was a multicenter, single-arm, first-in-human feasibility study conducted between Dec. 2, 2016 and March 8, 2017 in Europe. A total of 39 patients were treated with the Biosense Webster multi electrode radio frequency (RF) balloon catheter at four centers with nine different operators from both the U.S. and Europe.
The study showed the RF balloon catheter could deliver directionally-tailored energy using multiple electrodes for efficient acute PVI in patients with paroxysmal AF.
Traditional single point catheter ablation has a success rate of resolving AF in about 60 percent of patients. It is common to have patients come back for repeat ablations. Part of the issue is that completing a solid circle of ablation around the pulmonary veins can be difficult in a beating heart. Traditional catheter ablation procedures also can take hours. Balloon ablation devices can deliver a “one-shot” delivery of energy to complete the ablation in minutes. However, these devices have one major drawback, in delivering a uniform ablation around the entire balloon, which can cause damage to underlying critical structures like the esophagus or phrenic nerve, said Vivek Reddy, director of Cardiac Arrhythmia Services for the Mount Sinai Hospital and the Mount Sinai Health System and study investigator.
“Existing balloon catheters are limited in a number of ways, the most significant limitation being a single ablative element that delivers identical amounts of energy along the full pulmonary vein ostium circumference,” Reddy said. “This can lead to over-ablation of thin tissue, under-ablation of thick tissue, and unnecessary complications. The investigational RF balloon is designed to both optimize safety and efficacy and reduce procedure time.”
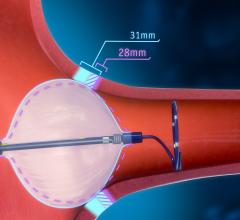
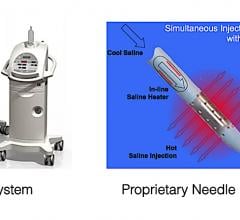
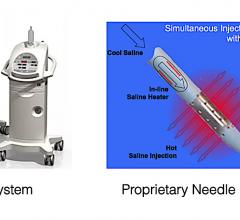
The Biosense Webster RF balloon has 10 electrodes around the balloon, which can be programmed to deliver different energy levels to prevent deeper ablation damage to surrounding tissue. Reddy said this allows operators to directionally tailor the energy delivery.
Results showed the RF balloon catheter was able to achieve electrical isolation of all pulmonary veins with a high rate of first-pass isolation and low evidence of latent pulmonary vein re-conduction. Reddy said 80 percent of the views were isolated on the first shot of energy. The procedural performance with the device was favorable, with 100 percent of the treated pulmonary veins electrically isolated without the need for a focal ablation catheter.
About the RADIANCE Study
Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation patients were treated with an investigational Biosense Webster RF balloon catheter with 10 irrigated, flexible gold surface electrodes intended to independently deliver varying amount of power. Patients underwent pulmonary vein isolation where RF energy was delivered simultaneously from all electrodes – up to 30 seconds posteriorly and 60 seconds anteriorly.
The primary endpoint was the incidence of primary procedure-related adverse events occurring within seven days of the procedure. Of note, any pulmonary vein stenosis, unresolved diaphragmatic paralysis or atrio-esophageal fistula that occurred also were analyzed as primary adverse events regardless of timing. Secondary endpoints included serious adverse events occurring over the course of the study and the effectiveness of electrical pulmonary vein isolation despite provocative pharmacological challenge.
In addition, the study included:
• Pre-procedure (baseline) testing included: a 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG), transthoracic echocardiogram, cardiac computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), a cerebral MRI, and a neurological exam with administration of the NIH Stroke Scale.
• Repetition of the 12-lead ECG, transthoracic echocardiogram, cerebral MRI and the neurological exam with the NIH Stroke Scale post-procedure (prior to hospital discharge).
• Post-procedure: Esophageal endoscopy of all patients to assess for any evidence of thermal esophageal damage.
For more information: www.biosensewebster.com.


 October 10, 2023
October 10, 2023