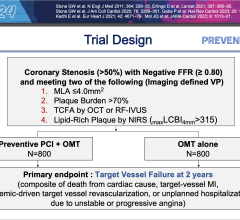
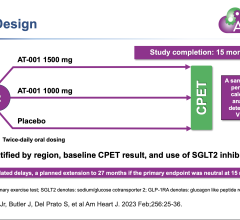
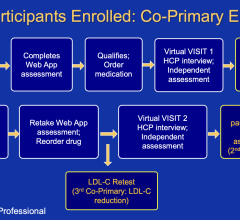
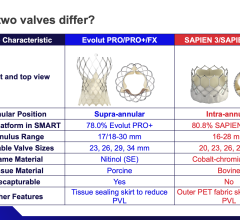
July 13, 2016 — Physicians may be drawing conclusions too soon about survival outcomes of patients who suffered a cardiac arrest outside the hospital. A study led by Bentley Bobrow, M.D., professor at the University of Arizona Colleges of Medicine in Tucson and Phoenix and co-director of the Arizona Emergency Medicine Research Center – Phoenix, and his fellow UA emergency medicine researchers, showed that physicians may need to allow comatose cardiac arrest patients much more time to awake before making a prognosis.
More than 400,000 Americans experience out-of-hospital cardiac arrest annually. Survival statistics are bleak: Although approximately 50 percent of people who arrest are revived after attempted resuscitation, only about 10 percent of these survive to leave the hospital. Furthermore, almost half of the survivors suffer some level of brain impairment from hypoxia (when the brain is not getting enough oxygen).
While out-of-hospital cardiac arrest is still a leading cause of death in the United States, outcomes have improved dramatically in places like Arizona, where the focus has been on innovative healthcare advances, Bobrow said. Advances include compression-only cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) training for the public, enhanced telephone-CPR instructions and training for 911 dispatchers, implementing high-performance CPR for EMS providers and making sure patients are taken to specialized hospitals that deliver treatments like targeted therapeutic hypothermia to improve brain recovery.
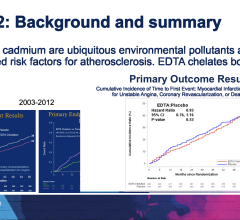
Results from the multicenter study, recently published in the Annals of Emergency Medicine, showed for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest patients, the time it takes to regain consciousness after rewarming from therapeutic hypothermia treatment varies widely and is longer than many had thought.
“Most patients are comatose after resuscitation and accurately predicting those who will wake up can be extremely challenging,” Bobrow said.
“There are many factors involved, but we know that it is common for doctors to try to decide who will and who won't wake up after 24 to 48 hours of hospitalization. However, our study found that a substantial number of cardiac arrest victims wake up longer than many people would expect. Sometimes they awaken from coma five, six or seven days after being admitted to the hospital and many of these have a good neurological outcome,” he said.
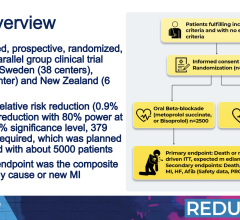
Among 573 out-of-hospital cardiac arrest patients who completed targeted temperature management, 60 woke up at least 48 hours after rewarming. Eight patients became responsive more than seven days after rewarming, six of whom were discharged with good neurological scores. One of the important findings was no predictive factors reliably identified who would awaken early or late.
Bobrow said, "We were surprised by the large proportion of cardiac arrest survivors who woke up more than three days after their arrest and went home with their families.
“While targeted therapeutic hypothermia has been shown to improve outcomes, no validated system currently exists for predicting when patients receiving this treatment will awaken from coma. Physicians and family members may need to wait longer than the traditional three days before making irrevocable decisions about brain function recovery and possible withdrawal of care,” he said.
In one example, Gary Brauchla, 68, went into cardiac arrest as he slept in his home in Pearce, Ariz., in 2012. Brauchla’s wife, Kathie, who is a former surgical technician, immediately called 911 and started CPR. Fifteen minutes later, paramedics took over administering CPR and shocked his heart with a defibrillator, restoring his heart rhythm.
Though Brauchla’s heart was restarted, he remained in a coma as he was flown by helicopter to Tucson. There, doctors treated him with coronary stents and therapeutic hypothermia to reduce his brain’s need for oxygen and minimize the risk of brain injury.
“The doctors said it usually takes up to 48 hours for people to wake up, but after two days he still was not responding,” said Kathie.
Brauchla remained in a deep coma, until finally, 72 hours later after he was rewarmed, he gradually began to awaken.
“After 48 hours, doctors used to start talking about pulling the plug,” said Kathie.
When Brauchla first woke up, he struggled with some neurological issues, but continued to improve. Since then, he has fully recovered and so far has ran 12 5K races. He now serves as the president of the newly formed Arizona Cardiac Arrest Survivors Group. In this role, he speaks to patients and their families, teaches bystander CPR classes and works to get more AEDs into the community.
Brauchla’s message to families, physicians and emergency medical personnel: “Everyone needs to be able and willing to do bystander CPR. And then, don’t give up!”
“Our study quantifies the timing of awakening from a coma after cardiac arrest in the era of targeted temperature management, and this timing is much different than before we had this treatment," said Daniel Spaite, M.D., UA professor and Virginia Piper Distinguished Chair of Emergency Medicine.
For more information: www.uahs.arizona.edu

 April 11, 2024
April 11, 2024