Siemens' MAGNETOM Espree is a 1.5T open-bore MRI.
Atrial fibrillation (AF) affects more than 3.5 million Americans and is a major source of strokes and a precursor to potentially fatal deterioration of the heart. Although physicians in the last decade have treated the condition with radiofrequency ablation, overall success rates have been limited. A 2007 report of the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) Task Force on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation noted that results are widely variable, due in part to differences in technique, follow-up, definitions of success, use of anti-arrhythmic therapy and in the experience and technical proficiency of the electrophysiologist.
A new approach that uses MRI as a pre-procedure diagnostic tool to visually demonstrate AF’s progression and location was presented as a poster at the American College of Cardiology (ACC) annual meeting in Chicago, IL, March 29 - April 1, 2008, by Nassir Marrouche, M.D., the director of the Atrial Fibrillation Program at the University of Utah School of Medicine.
MRI to facilitate AF treatment
In a study entitled “MR Imaging in the Electrophysiology (EP) Laboratory,” in which Dr. Marrouche is one of the authors, researchers note some of the challenges in treating AF include “efforts to maximize efficacy and safety, improve operator skills, better characterize left atrial anatomy and improve navigation within the cardiac chambers.”
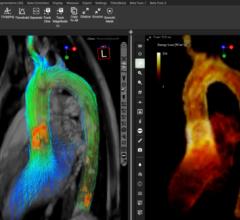
In many cases, the applied treatment strategies to minimize the electrical effects of the pulmonary veins in AF have utilized a mapping catheter under fluoroscopic guidance to electrically isolate the pulmonary veins (PV) from the rest of the left atrium (LA). But the doctors in this study decided to integrate three-dimensional (3D) MRI to improve navigation in procedures requiring substrate-based ablation, for follow-up and localizing causes of post-procedural complications. “MRI offers the most detailed anatomic and physiologic information about normal and damaged myocardial tissue,” said Dr. Marrouche. The study concurs that “MRI...has vastly superior soft tissue contrast when compared to fluoroscopy and CAT scans and does not expose the patient to ionizing radiation.”
During the ablation procedure, Dr. Marrouche notes that MR angiograms help to improve anatomical maps, which are used in conjunction with other imaging modalities to determine appropriate sites for ablation. The modality also has very important roles in post-procedural assessment and follow-up, using delayed enhancement.
MRI outshines other imaging techniques
In comparing MRI to transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE), researchers were concerned with the invasiveness of TEE and that the complex morphology of the left atrial appendage may result in underestimation of the thrombus using TEE.
The researchers found that cardiac MRI allows for a convenient and useful alternative to TEE. “It is noninvasive, allows evaluation of cardiac morphology without any assumptions in regard to cardiac geometry and can be taken at the same time as other studies that are necessary for planning of the RF ablation procedure,” the study said. Adding, “In recent studies, MRI successfully detected thrombus with 100 percent sensitivity (verified utilizing TEE).” For treating AF, MRI demonstrated its
usefulness in preparing patients for the initial treatment “by helping to localize left atrial thrombus and defining anatomy of pulmonary veins, left atria and the surrounding structures.”
When performing radiofrequency ablation in the LA, where there is the possibility of damaging adjacent structures with potentially deadly side effects, they found “MRI serves an essential point in the planning of the procedure.”
In the cath lab, the researchers tested MRI utilization in periprocedure merged image navigation and for MRI and electroanatomic mapping systems. They found that “electroanatomic mapping systems, which allow for high-resolution MRI images to be merged with electrophysiological data acquired during the ablation procedure, help to alleviate some of the potential complications. The electroanatomic model also helps the physician performing the procedure to guide the catheter manipulation near pulmonary vein ostia and other complex structures, while helping to ascertain complications, which may involve other structures of concern such as the esophagus or aorta.”
The researchers believe that by building on the progress of other groups that have successfully applied MRI technology to interventional procedures targeting the ventricle, it will be possible to assess lesion size and change in tissue pathology in real time. They believe these steps will serve to greatly increase the curative rate for AF while simultaneously decreasing the complication rate.
Future applications of MRI for AF
At Heart Rhythm 2008, Dr. Marrouche will present findings from his animal studies on how MRI angiograms can be used effectively to monitor the effects of radiofrequency ablation on heart tissue during a procedure. Other research findings include the use of delayed-enhancement MRI imaging to assess scars and other collateral damage following a procedure, which will likely prove valuable in diagnosing post-procedural complications. As interventional MRI scanners become available, the study said, “MRI will become even more important than it now is in the treatment of atrial fibrillation patients.”
Dr. Marrouche is currently developing technology that can provide the imaging of scar tissue in real time using MRI. Within a single display, it will be possible to show lesion size and location and its relation to existing abnormal tissue. “In the future, the use of real-time MRI imaging may allow for accurate assessment of the catheter position in relation to the pulmonary veins, other key left atrial structures and the esophagus,” the study concluded. “Furthermore, histology-like imaging of lesion size, location and the identification of the presence of anatomic gaps between lesions will likely improve the formation of contiguous lines and thus improve efficacy,” indicated the study. This technique, Dr. Marrouche hopes, will prove valuable in diagnosing post-procedural complications and determining how they may be related to the RF parameters, which, he adds, will “greatly improve the success rate in complex patients.”
Reference: Robert S. Oakes, M.D.; Nassir F. Marrouche, M.D.; Rob S. MacLeod; et al. MR Imaging in the Electrophysiology (EP) Laboratory, A Novel Method to Facilitate Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation.www.siemens.com/magnetom-world. 2007; 74-77.


 January 21, 2026
January 21, 2026