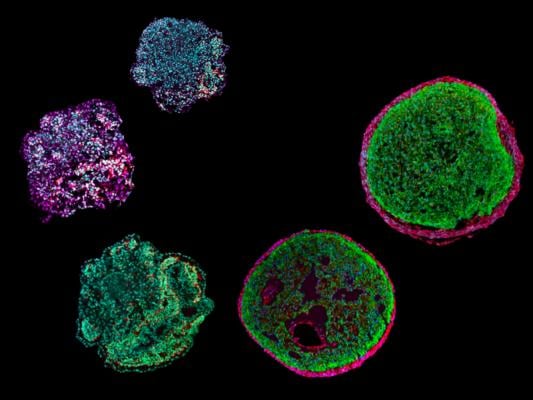
A team from the Technical University of Munich (TUM) has suggested using stem cells to replicate the development of the human heart. The result is an organoid, a kind of miniature heart. This allows the earliest phase of the formation of our heart to be studied and diseases to be researched. Use free for reporting on the TUM if the copyright is named. A team at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) has induced stem cells to emulate the development of the human heart. The result is a sort of “mini-heart” known as an organoid. It will permit the study of the earliest development phase of our heart and facilitate research on diseases. Image courtesy of TUM
April 4, 2023 — A team at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) has induced stem cells to emulate the development of the human heart. The result is a sort of “mini-heart” known as an organoid. It will permit the study of the earliest development phase of our heart and facilitate research on diseases.
The human heart starts forming approximately three weeks after conception. This places the early phase of heart development in a time when women are often still unaware of their pregnancy. That is one reason why we still have little knowledge of many details of how the heart is formed. Findings from animal studies are not fully transferable to humans. An organoid developed at TUM could prove helpful to researchers.
A Ball of 35,000 Cells
The team working with Alessandra Moretti, Professor of Regenerative Medicine in Cardiovascular Disease, has developed a method for making a sort of “mini-heart” using pluripotent stem cells. Around 35,000 cells are spun into a sphere in a centrifuge. Over a period of several weeks, different signaling molecules are added to the cell culture under a fixed protocol. “In this way, we mimic the signaling pathways in the body that control the developmental program for the heart,” explains Alessandra Moretti. The group has now published its work in the journal Nature Biotechnology.
First-Ever “Epicardioids”
The resulting organoids are about half a millimeter in diameter. Although they do not pump blood, they can be stimulated electrically and are capable of contracting like human heart chambers. Prof. Moretti and her team are the first researchers in the world to successfully create an organoid containing both heart muscle cells (cardiomyocytes) and cells of the outer layer of the heart wall (epicardium). In the young history of heart organoids – the first were described in 2021 – researchers had previously created only organoids with cardiomyocytes and cells from the inner layer of the heart wall. (endocardium).
“To understand how the heart is formed, epicardium cells are decisive,” says Dr. Anna Meier, first author of the study. “Other cell types in the heart, for example in connecting tissues and blood vessels, are formed from these cells. The epicardium also plays a very important role in forming the heart chambers.” The team has appropriately named the new organoids “epicardioids”.
New Cell Type Discovered
Along with the method for producing the organoids, the team has reported its first new discoveries. Through the analysis of individual cells they have determined that precursor cells of a type only recently discovered in mice are formed around the seventh day of the development of the organoid. The epicardium is formed from these cells. “We assume that these cells also exist in the human body – if only for a few days,” says Prof. Moretti.
These insights may also offer clues as to why the fetal heart can repair itself, a capability almost entirely absent in the heart of an adult human. This knowledge could help to find new treatment methods for heart attacks and other conditions.
Producing “Personalized Organoids"
The team also showed that the organoids can be used to investigate the illnesses of individual patients. Using pluripotent stem cells from a patient suffering from Noonan syndrome, the researchers produced organoids that emulated characteristics of the condition in a Petri dish. Over the coming months the team plans to use comparable personalized organoids to investigate other congenital heart defects.
One Objective: Reducing Animal Experiments
With the possibility of emulating heart conditions in organoids, drugs could be tested directly on them in the future. “It is conceivable that such tests could reduce the need for animal experiments when developing drugs,” says Alessandra Moretti.
Organoid Research is a Key Research Area at TUM
The researchers have registered an international patent for the process of creating heart organoids. The Epicardioid model is one of several organoid projects at TUM. At the Center for Organoid Systems work groups from various departments and chairs will collaborate. They will conduct interdisciplinary research into pancreas, brain and heart organoids with state-of-the-art imaging and cellular analysis to study the formation of organs, cancer and neurodegenerative diseases and achieve progress for medicine with human 3D systems.
For more information: https://www.tum.de/en/


 January 05, 2026
January 05, 2026 









