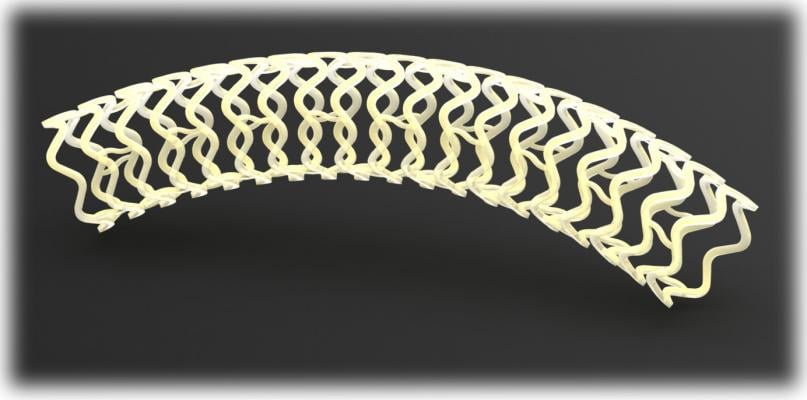
Image courtesy of Reva
December 31, 2014 — Reva Medical initiated patient enrollment with its Fantom bioresorbable drug-eluting scaffold. The first patient implants were performed by Alexandre Abizaid, M.D., director of Invasive Cardiology at Institute Dante Pazzanese of Cardiology in Sao Paulo, Brazil. Abizaid is co-principal investigator for the Fantom clinical trial program. Jeff Anderson, Reva's senior vice president of Clinical and Regulatory Affairs, as in previous clinical studies, was present for the implants. "The scaffold was easily delivered and the procedure was aided by the visibility of the scaffold under X-ray, a feature that we believe provides physicians with a valuable tool for confirming proper placement during implant," says Anderson.
Fantom is a fully bioresorbable sirolimus-eluting coronary scaffold that is designed to dissolve over time, leaving the artery free of a permanent implant and thereby allowing the artery to return to its vasomotion. Fantom is made from Reva's proprietary polymer that was developed specifically for scaffold performance. The properties of Reva's polymer provide for excellent scaffold strength in a thin-strut design, ease-of-use features like single-step inflation and complete visibility of the scaffold under X-ray, an attribute unique to Reva among bioresorbable scaffolds.
For more information: www.teamreva.com


 January 05, 2026
January 05, 2026 









