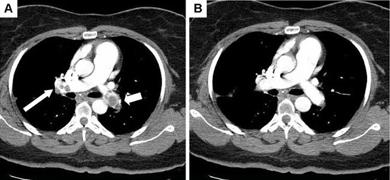
November 23, 2010 - A new technique that combines the heat and energy of ultrasound with the highly targeted delivery of clot-busting drugs appears to be effective at treating patients with acute massive pulmonary embolism (PE).
The new treatment, called ultrasound-accelerated catheter-directed thrombolysis (CDT), was developed by the Ekos Corporation.
It adds a new dimension to conventional CDT, in which clot-busting medication is delivered directly to the embolus over an extended period of time through an infusion catheter. In ultrasound-accelerated CDT, the infusion catheter includes an element device that emits ultrasound energy in the therapeutic zone. The ultrasound makes the clot more porous and penetrable, thus lessening both the length of time of the infusion and the volume of thrombolytic drug applied.
Of 46 patients treated for massive PE, Peter Lin, M.D., professor of surgery at the Baylor College of Medicine, reported that ultrasound-accelerated CDT achieved complete thrombolysis in 100 percent of the patients treated compared to 67 percent patients receiving CDT without ultrasound. Both the average dose of thrombolytic agent and the length of time for infusion were lower for patients receiving ultrasound-accelerated CDT. Furthermore, there were no hemorrhagic complications within this group compared to 3 incidents in the CDT group. All patients receiving ultrasound-accelerated CDT were treated with tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) as the thrombolytic agent. tPA was administered in 16 of the 21 patients undergoing CDT, with urokinase as the thrombolytic for the other five.
“While both CDT and ultrasound-accelerated therapy have remarkable therapeutic effects for this life threatening condition, the EKOS device provides a significant added benefit of clearing most if not all the clot while using less drug,” Lin said. “In institutions with appropriate clinical expertise, ultrasound-accelerated thrombolytic is a beneficial treatment option in patients who have acute massive PE with contraindications to systemic thrombolysis, when time to administer systemic thrombolytic agents is lacking, or when no improvement follows stand intravenous thrombolytic administration.”
For more information: www.VEITHpress.org


 January 05, 2026
January 05, 2026 









