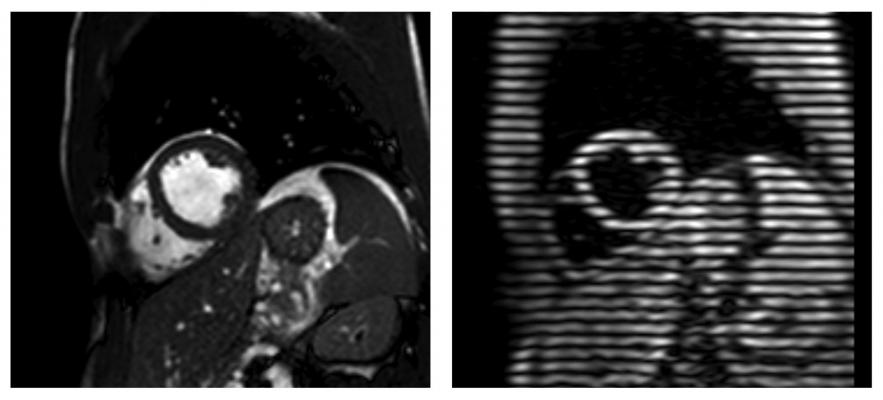
August 29, 2018 — A newly developed rapid cardiac imaging protocol quickly and cheaply diagnosed heart ailments in patients in Peru, according to new research in Journal of the American Heart Association1.
In Peru, cardiovascular disease affects 3.2 million (16 percent of the adult population), leading to a significant loss of well-being, estimated at 281,829 Disability Adjusted Life Years.
Current cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMR) usage in high-income countries focuses on function, scar, perfusion, flow, mapping and angiography, and delivers valuable clinical insights leading to targeted and precise treatments. However, these varied techniques make it slow (typically 45 minutes), expensive, complex and potentially out of reach for most people in the developing world.
In this study, researchers developed and tested a rapid CMR protocol using contrast dye that measured cardiac structure, function and scarring. The rapid diagnostics worked with existing infrastructure, took 18 minutes and cost $150 per patient resulting in important changes in patient care.
“Our CMR strategy was three to five times cheaper than current CMR exams in Peru,” said James C. Moon, M.D., study lead author and professor at Barts Heart Centre, St. Bartholomew’s Hospital in London. “It also can be delivered two to three times faster and is easier than conventional CMR.”
Researchers conducted scans on 98 Peruvian patients (average age 52, 60 percent female). Scanning found 26 percent had hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, 22 percent had dilated cardiomyopathy and 15 percent had ischemic cardiomyopathy. Scans also uncovered 12 other pathologies including tumors, congenital heart disease, iron overload, amyloid plaques , genetic syndromes, inflamed vessels, clots and valve disease.
Researchers report CMR revealed an unsuspected new diagnosis in 19 percent of patients or led to a change of treatment in 37 percent. In 5 percent, a change in care management was suggested but not delivered due to access barriers (cardiac surgery or device therapy).
Researchers found rapid CMR satisfied all imaging needs in 89 percent of patients. In 7 percent where CMR was the first imaging technique performed, no further non-invasive imaging was needed. CMR did not miss any diagnoses initially found by echocardiography, researchers said.
“Because the rapid CMR protocol was embedded in clinical care with training and education, it resulted in important and frequent patient management changes that appeared beneficial for both patients and the healthcare system,” said Katia Menacho, Ph.D., study first author and cardiovascular science research fellow at Barts Heart Centre, St. Bartholomew’s Hospital in London. “Lack of resources is not a justification for the absence of key diagnostic tests in the developing world.”
In an accompanying editorial, Christopher M. Kramer, M.D., University of Virginia Health System in Charlottesville noted, “To make this proof-of-principle study a reality in much of the developing world, imagers will need to be trained at sites with appropriate scanner technology. Only in this way will an abbreviated protocol for evaluation of cardiomyopathies be implemented. This is an exciting time for the potential of broadening the impact of CMR throughout the developing world.”
For more information: www.ahajournals.org/journal/jaha
Reference
1. Menacho K., Ramirez S., Segura P., et al. INCA (Peru) Study: Impact of Non‐Invasive Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Assessment in the Developing World. Journal of the American Heart Association, Aug. 29, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.118.008981

 January 28, 2026
January 28, 2026