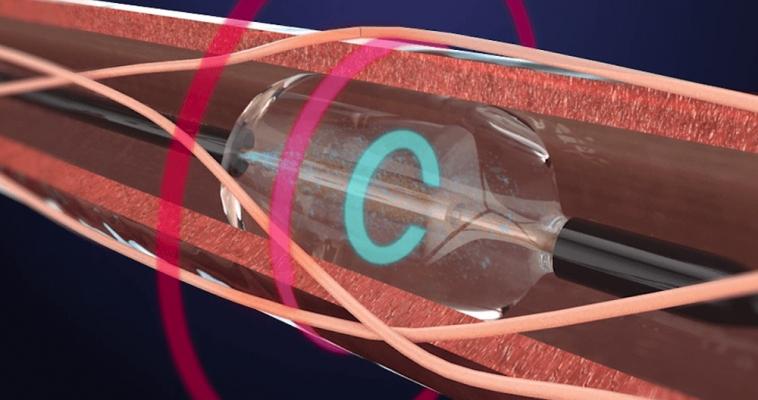
May 31, 2018 – ReCor Medical announced that the RADIANCE-HTN SOLO study met its primary efficacy endpoint and demonstrated a statistically significant reduction in blood pressure in hypertensive patients. In addition, the company announced submission of an investigational device exemption (IDE) supplement to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for a pivotal study of its Paradise System for the treatment of hypertension. Prof. Ajay Kirtane, M.D., of New York-Presbyterian Hospital/Columbia University has taken the role of co-principal investigator for RADIANCE-HTN.
Data presented at EuroPCR 2018, May 21-23 in Paris, France, with simultaneous publication in The Lancet, showed that RADIANCE-HTN SOLO met its primary efficacy endpoint. SOLO demonstrated a difference in ambulatory daytime systolic blood pressure changes between treatment and sham at 2 months of -6.3 mm Hg (p-value of 0.0001) with no major adverse events. Additional endpoints including office, home and 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure levels, and the percentage of patients with controlled blood pressure at 2 months, were also improved in the Paradise group relative to sham.
Watch a VIDEO on this an other renal denervation studies presented at PCR 2018.
“We are pleased with the outcomes of the RADIANCE-HTN SOLO trial,” commented co-principal investigator Prof. Laura Mauri, Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Boston. “We believe that SOLO was designed and conducted in a rigorous manner. In patients with mild to moderate hypertension, previously treated with up to two medications and randomized while off medications, the Paradise System reduced blood pressure in comparison to a sham control. In addition, the procedure was performed with an average ablation time of less than one minute and demonstrated a positive safety profile both acutely and at 30-day follow-up.”
Prof. Michel Azizi, Hôpital Européen Georges-Pompidou, Paris, France, co-principal investigator, commented, “The SOLO investigators are satisfied with the clinical outcomes in the study. At two months, more than 66 percent of subjects treated with renal denervation experienced a 5 mmHg or greater reduction in daytime ambulatory systolic blood pressure, compared with 33 percent in the sham group. RADIANCE-HTN SOLO also demonstrated a reduction in office blood pressure of 10 mmHg systolic which, if durable over time, has been shown to reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases, including stroke and heart attack, in patients with hypertension. The RADIANCE-HTN research program is ongoing, with extended follow-up for the SOLO patients and continued enrollment of the TRIO cohort patients with resistant hypertension. Our goal is to demonstrate the effectiveness, safety and durability of renal denervation in both important patient populations.”
ReCor also announced that the company submitted a new protocol to the FDA for a pivotal study: an independently-powered, sham-controlled, efficacy study of the Paradise System in patients with hypertension.
Other late-breaking trials presented at EuroPCR 2018.
For more information: www.recormedical.com


 January 05, 2026
January 05, 2026 









