Flexible electronics have been developed to implant in patients to constantly monitor their cardiac condition.
This is an overview of some of the biggest cardiology technology advances. These innovations are covered in more detail in the two-volume set titled "Emerging Technologies in Heart Diseases." These innovative technologies mark the midway of a technological revolution in patient care. Here are a list of 10 noteworthy new cardiac technologies:
1. Miniature Ventricular Assist Device
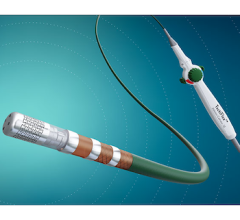
The emergence of a ventricular assist device (VAD) has revolutionized the care of patients with advanced heart failure. Primarily developed as a bridge to transplantation, the VAD has been shown to prolong life and to improve the quality of life when a donor heart is not found. Older versions required the implantation of a bulky pump and required patients to ambulate with heavy, large external batteries and control units. Yet, several revolutionary improvements in device size, battery reliability, and even wireless charging technologies might make these devices physically unnoticeable in the coming years, and possibly decrease patient susceptibility to infections. In addition, various mechanical modifications and newer modes of operation have limited the rates of hemolysis, thrombosis, and secondary aortic valve insufficiency.
Miniature VAD. Source: Watt et al. Artificial Mechanical Hearts and Ventricular Assist Devices. In: Emerging Technologies for Heart Diseases, Vol. 1 - Treatments for Heart Failure and Valvular Disorders. 2020; Elsevier, Academic Press (AP). Pages 25-40.
2. Novel Embolic Protection to Prevent Strokes
Atrial fibrillation (AF or AFib) remains a leading cause of stroke, which in turn may be associated with devastating health consequences and mortality. Yet, oral anticoagulants and left atrial appendage (LAA) occlusion devices may not be appropriate for all patients or may be associated with life-threatening complications. In recent years, novel, device-based technologies for stoke prevention have evolved. Some focused on carotid implants, while newer devices have been designed for continuous embolic filtration at the level of the common aortic pathway. These approaches, which are currently being tested in preclinical studies, might be translated in the near future to treatments available for patients with increased bleeding risks.
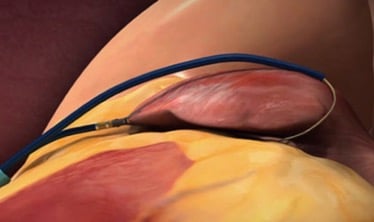
Lariat LAA closure device device (SentreHeart Inc, Redwood, Calif.). Source: Goel et al. Percutaneous closure of the left atrial appendage for stroke prevention. In: Emerging Technologies for Heart Diseases, Vol. 2 - Treatments for Myocardial Ischemia and Arrhythmias. 2020; Elsevier, Academic Press (AP). Pages 961-977.
Related LAA Occlusion Content:
VIDEO: Overview of Left Atrial Appendage (LAA) Closure Technology and New Innovations — Interview with Horst Sievert, M.D.
COVID-19 Boosts Demand for Left Atrial Appendage Closure Devices Market
VIDEO: Overview of LAA Occlusion Using the Watchman FLX — Interview with Devi Nair, M.D.
3. Organ Conformal Electronics
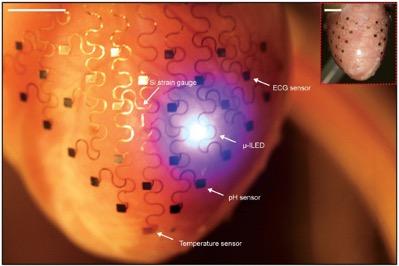
Conformal electronics are flexible, stretchy, electronic devices that can diagnose and treat tissue malfunctions. They have high spatiotemporal resolution and are comprised of a system of various sensors and transducers. Conformal electronics assess multiple parameters to monitor and regulate cardiac tissue functions by following the shape of the epicardium or endocardium. The technology of conformal electronics can transform the current model of cardiac diagnostics and therapeutics by enabling the development of new equipment. Also, new minimally invasive methods to access the epicardial tissue are likely to facilitate clinical adoption of this technology.
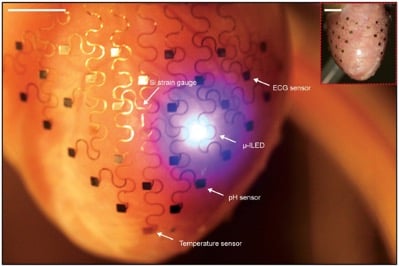
Flexible electronics attached to the heart for cardiac monitoring. Source: Yin et al. Organ Conformal Electronics for Cardiac Therapeutics. In: Emerging Technologies for Heart Diseases, Vol. 2 - Treatments for Myocardial Ischemia and Arrhythmias. 2020; Elsevier, Academic Press (AP). Pages 911-937.
Related Flexible Electronics in Cardiology Content:
Flexible Electronics for Wearable Cardiac Monitoring Technologies
Flexible Electronics Mounted on Balloons May Improve Cardiac Catheter Ablation Procedures
4. Mitral Valve Modulation and Repair
Transcatheter Mitral Valve Repair (TMVR) technologies are expanding rapidly. They have the potential to become alternatives to surgery for specific patients. TMVR devices can be differentiated according to the portion of the mitral valve they are intended to repair: the leaflet, the annulus, or the chordae, and to remodel the ventricles. To date, early results of novel TMVR technologies seem promising but the long-term sustainability and effectiveness have not been determined. Yet, given the advancements in transcatheter technologies, it is convincible that in the future, mitral regurgitation will be treated mainly using a minimally invasive approach.
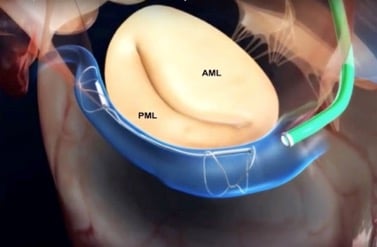
Carillon Mitral Contour System from Cardiac Dimensions can can be implanted for to reshape the annulus using TMVR. Source: Colli et al. Transcatheter Mitral Valve Therapies for Degenerative and Functional Mitral Regurgitation. In: Emerging Technologies for Heart Diseases, Vol. 1 - Treatments for Heart Failure and Valvular Disorders. 2020; Elsevier, Academic Press (AP). Pages 417-461.
Related TMVR Content:
VIDEO: Interventional Structural Heart Advances Are Rapidly Expanding — Interview with Juan Granada, M.D.
Developments in Transcatheter Mitral Valve Replacement
VIDEO: Transcatheter Mitral Valve Replacement Planning — Interview with Joao Cavalcante, M.D.
5. Cardiac Decellularization and Engineered Heart Tissue
Tissue engineering techniques that use cells and regenerative medicine to treat heart disease, are promising new approaches in cardiovascular research. Scaffolds (i.e., biomaterials used as supports), cells and appropriate growth factors are needed to enable reconstruction of new tissue. Because the biomaterial is integral to the functional integrity and attachment of human cells, generating the ideal scaffold remains one of the most challenging aspect of tissue engineering. A decellularized heart composed of native extracellular matrix can provide a complex, unique, and natural scaffold that offers the physical and chemical signals required for cardiac function.
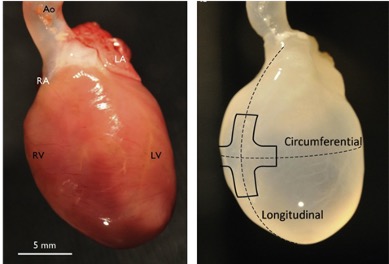
Isolated cadaveric heart prior to and following decellularization. Source: Taylor, et al. Decellularization of Whole Hearts for Cardiac Regeneration. In: Emerging Technologies for Heart Diseases, Vol. 1 - Treatments for Heart Failure and Valvular Disorders. 2020; Elsevier, Academic Press (AP). Pages 291-310.
Related Extracellular Matrix Content:
FDA Clears CorMatrixCanGaroo ECM Envelope For Implantable EP Devices
Heart Failure Cardiac Function Improved With Extracellular Matrix With LVAD
6. Small, Portable ECMO Devices
Patients with hemodynamic compromise may not be optimally balanced with an intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP). Therefore, various devices have been developed to provide other advanced measures of circulatory support. Although most centers have limited experience with these devices, they may be lifesaving in specific patients. Also, extracorporeal oxygenation (ECMO) provides patients the opportunity to avoid mechanical ventilation. This will prevent possible decreases in blood pressure due to anesthesia and reduced venous return. Small, portable devices aimed at providing ventilatory and circulatory support are being developed for these critical cases.
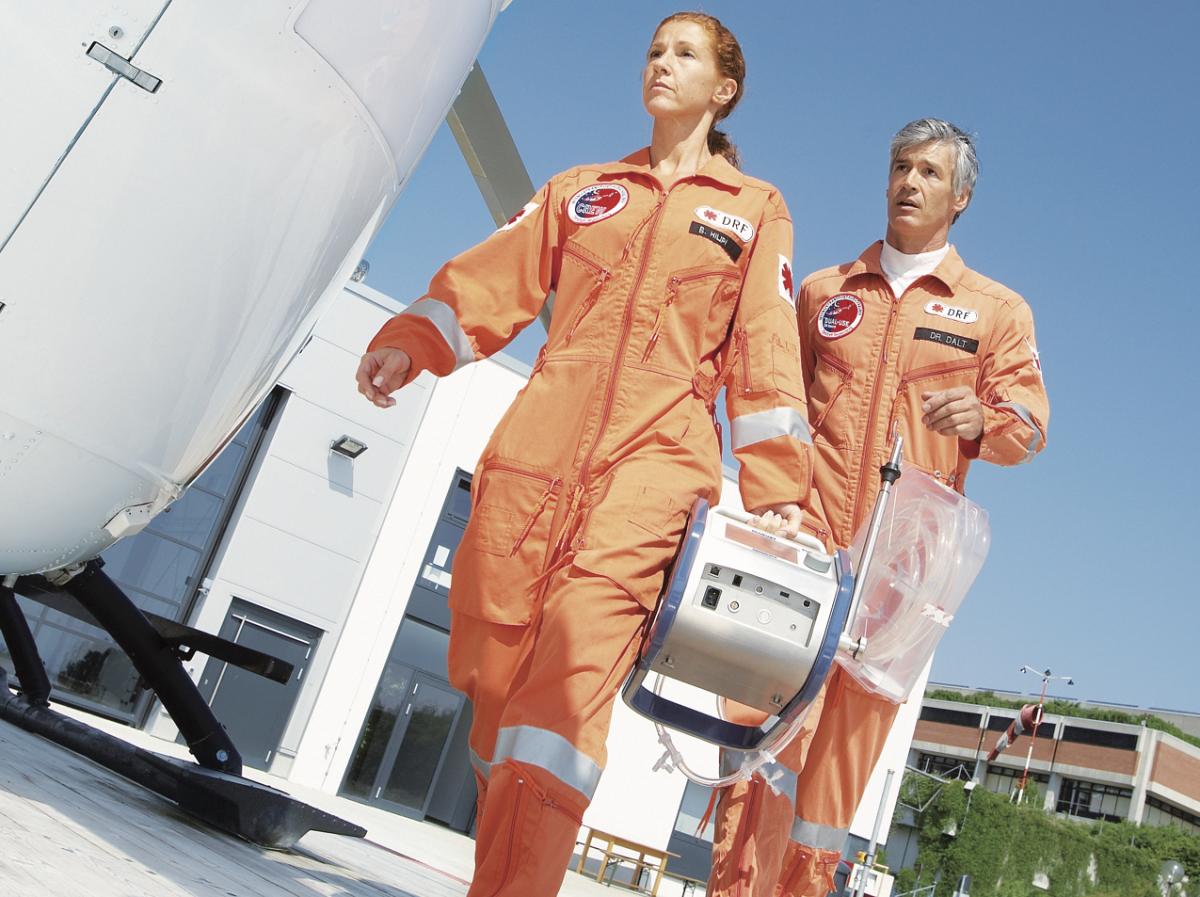

The Maquet CardioHelp ECMO system is an example of a small, lightweight, portable ECMO.
Related ECMO Systems Content:
ECMO May Become the pVAD of the Future
Abiomed Adds ECMO Cardiopulmonary Support to its Portfolio
7. Engineered Heart Valve
The global burden of congenital or acquired heart valve defects is high. Bioprosthetic or mechanical replacement valves are often used, although they have limitations. This is especially true for pediatric patients who continue to grow. A potential solution is developing an in situ tissue engineering approach. A synthetic, bioresorbable scaffold might lead to individualized replacements for heart valves. These might be less prone to infections and more suitable for pediatric populations.
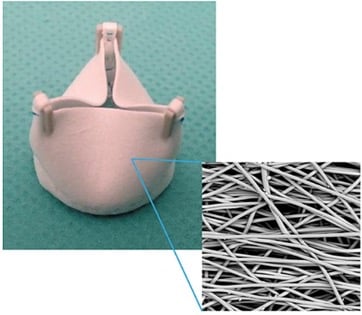
Bioresorbable synthetic scaffold generated using electrospinning techniques. Source: Klouda et al. Heart Valve Tissue Engineering: Current Preclinical and Clinical approaches. In: Emerging Technologies for Heart Diseases, Vol. 1 - Treatments for Heart Failure and Valvular Disorders. 2020; Elsevier, Academic Press (AP). Pages 383-398.
Related 3-D printing Content:
The Future of 3-D Printing in Medicine
World’s Smallest Intravascular OCT Imaging Device Created Using 3-D Printing
Researchers 3-D Print a Beating Heart From Human Cells
New Technique Allows More Complicated 3-D Bioprinting
The Use of 3-D Printing in Cardiology
8. Artificial Intelligence to Predict Cardiac Arrhythmias
Cardiac arrhythmias are a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Although rhythm disorders may be efficiently treated with implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs), the ability to accurately determine which patients will benefit from these measures is currently limited. Also, in patients who do not have an intracardiac device, delivery of external defibrillatory shocks shortly after the onset of arrhythmia may be lifesaving. Therefore, many efforts are invested in increasing the ability to predict upcoming events and calling for medical assistance. Computational tools generally known as artificial intelligence (AI) may soon enhance our ability to predict the occurrence of life-threatening arrhythmias and thereby, provide earlier preventive and the therapeutic interventions. The increase in the use of wearable cardiac monitoring devices and the ability to provide advanced analysis of ECG and other electrophysiological data are expected to further revolutionize the field of machine learning-based diagnostics in cardiology.

The consumer-grade Fitbit Sense offers AI to automatically detect atrial fibrillation. Read more in the article Fitbit ECG App to Identify Atrial Fibrillation Receives Regulatory Clearance in U.S. and Europe.
Related Content on Wearables and Big Data in Healthcare:
Tracking Cardiovascular Health Population Trends Using Consumer Wearables
Bristol-Myers Squibb-Pfizer Alliance, Fitbit Team Up on Atrial Fibrillation Detection
Artificial Intelligence Detects AFib Using Apple Watch Heart Rate Sensor
Consumer Smart Watches Accurately Measure Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia
VIDEO: Use of Wearables to Track Electrophysiology Patients — Interview with Khaldoun Tarakji, M.D.
VIDEO: The Future of Wearables in Healthcare — Karl Poterack, M.D.
9. Magnetic Navigation and Robotic Systems
Catheter ablation is used to prevent ventricular arrhythmias by damaging or destroying the causative tissue. Due to difficulties targeting the appropriate tissue, advanced technologies are needed. Electrophysiologic mapping has advanced significantly along with the techniques and tools that can be used to effectively eliminate the arrhythmic substrate. Combining these tools in the electrophysiology (EP) lab with robotic navigation systems may lead to more precise ablation procedures for difficult cases, while reducing exposure to radiation.
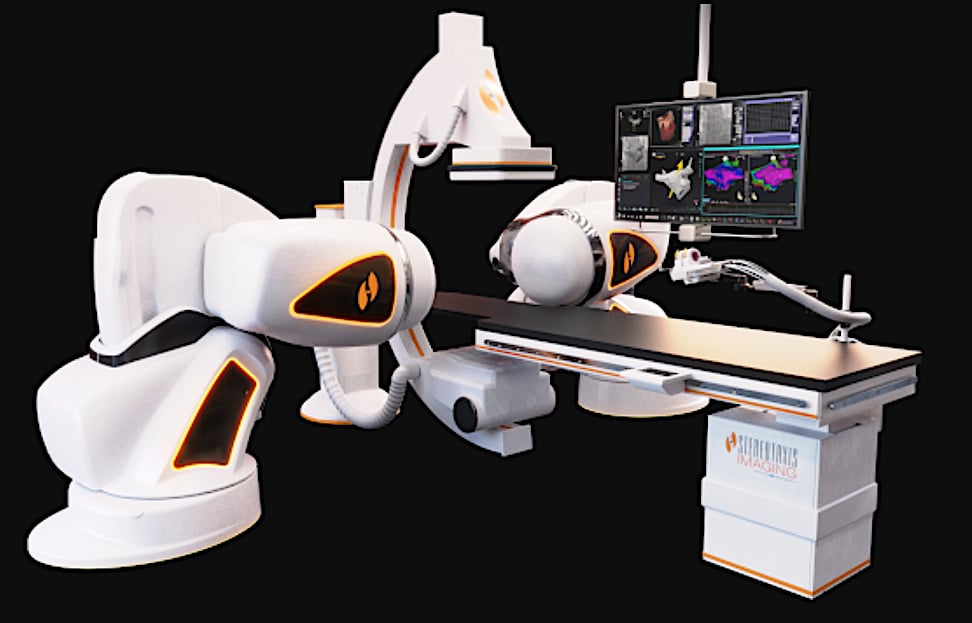
Stereotaxis Genesis Robotic Magnetic Navigation System, the latest system from the vendor with its first two installs taking place in 2020. Source: AbdelWahab et al. Electrophysiologic Mapping and Cardiac Ablation therapy for Prevention of Ventricular Tachycardia. In: Emerging Technologies for Heart Diseases, Vol. 2 - Treatments for Myocardial Ischemia and Arrhythmias. 2020; Elsevier, Academic Press (AP). Pages 683-723.
Related Robotic EP Lab Content:
VIDEO: Virtual Tour of the Robotic Electrophysiology Lab at Banner Health
VIDEO: Advantages of Robotic Ablation in the EP Lab — Interview with Peter Weiss, M.D.
Time to Take Another Look at Robotics in Electrophysiology
10. Pluripotent Stem Cells and Transdifferentiated Cardiomyocytes
Cardiac devices may be associated with complications including repeated need for battery replacement, lead failure, infections, and limited applicability in young patients. Recent, major breakthroughs in induced pluripotent stem cells technologies and transdifferentiation approaches may revolutionize treatment of bradyarrhythmias and heart failure. Ventricular and pacemaker cells have been generated both in vitro and in vivo in preclinical models. Upscaling technology based on cell (and gene) grafts to the organ level, ensuring graft survival, and guaranteeing long-term safety are needed before these innovative methods can be used to replace electrical cardiac pacemakers and to treat patients with heart failure.
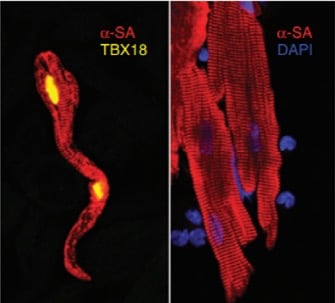
TBX18 over expression induces transdifferentiation of cardiac myocytes towards pacemaker-like cells. Source: Végh et al. Molecular therapies for bradyarrhythmias. In: Emerging Technologies for Heart Diseases, Vol. 2 - Treatments for Myocardial Ischemia and Arrhythmias. Elsevier, Academic Press (AP). Pages 811-840.
Related Cardiac Stem Cell Content:
Scientists Discover New Type of Immune Cells Essential for Forming Heart Valves
Alabama Scientist Custom-Engineering Living Tissue to Fix a Heart
Wisconsin Researchers Transform Common Cell to Master Heart Cell
FDA Says Adult Stem Cell Research Shows Promise
About the author: Udi Nussinovitch M.D., Ph.D., is the editor of the two-volume set titled "Emerging Technologies in Heart Diseases Vol. 1" and "Emerging Technologies in Heart Diseases Vol. 2." The books cover all the major technologies in use or under development, for the treatment of cardiovascular disorders. The books present information systematically and are the only reference that attempts to address the technological aspects of cardiovascular treatments. They present a very interesting read for anyone involved in the biomedical field, cardiovascular researchers and cardiologists, who aspire to learn about currently available technologies as well those in the pipeline.
Nussinovitch graduated from the Sackler Faculty of Medicine, Tel Aviv University, and received training at the Sheba Medical Center, Rambam Healthcare Center and Meir Medical Center, while concurrently earning a Ph.D. in cardiac electrophysiology from the Technion Institute of Technology, Haifa, Israel. Dr. Nussinovitch has dedicated his research to investigating novel therapeutic approaches for cardiac disorders and modulating the cardiac electrophysiologic substrate for therapeutic purposes. He is the Director of the Applicative Cardiovascular Research Center (ACRC), affiliated with Tel Aviv University. Dr. Nussinovitch founded several biotech companies, including InVatin Technologies and InSpira Oxygenation Technologies. He performs his clinical work at Meir Medical Center, a medical facility and leading referral center in Israel.
Related Future Technologies in Cardiology and Healthcare Content:
8 Cardiovascular Technologies to Watch in 2020
Cleveland Clinic Unveils Top 10 Medical Innovations for 2020
The Future of Cardiology: 17 Technologies to Watch
Cardiovascular Advances to Watch in the Next Decade
VIDEO: Editor's Choice of Future Healthcare Technologies at HIMSS
Cardiovascular Advances to Watch in the Next Decade
A 40,000 Foot View of Trends in Cardiology
New Technology Highlights on the ACC 2019 Exhibit Floor
6 Key Health Information Technology Trends at HIMSS 2019
Echocardiography Trends at ASE 2019
7 Hot Topics in Cardiac CT Imaging
Key Technology and News at AHA 2018
6 Hot Topics in Interventional Cardiology at TCT 2019
VIDEO: Editor's Choice of the Most Innovative New Cardiac Technology at AHA 2018
Cardiovascular Advances to Watch in the Next Decade


 February 06, 2026
February 06, 2026