February 1, 2018 –Stereotaxis, who makes innovative robotic technologies for the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias, announced that the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) has published a consensus document endorsed by the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) highlighting the occupational risk of radiation exposure in the electrophysiology laboratory and presenting several ways to reduce that exposure.
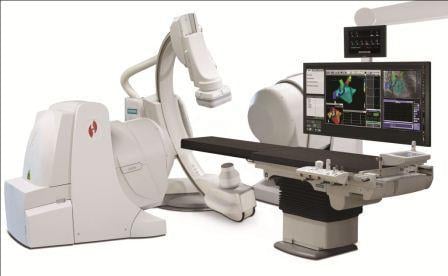
The occupational hazards to physicians and cath lab workers have been well documented in the literature. The EHRA consensus document states that “electrophysiology and training in electrophysiology may be associated with significant occupational radiation exposure.” Included in a list of recommendations for reduction of fluoroscopy exposure is the use of remote navigation systems such as the Niobe magnetic navigation system from Stereotaxis.
Unlike most recommendations, which reduce radiation exposure, the EHRA consensus document describes remote navigation systems as allowing for “near zero exposure to operator(s).” The paper states that personnel in the electrophysiology laboratory who are positioned in the control room are protected by both shielding and distance from the X-ray beam, and that radiation exposure in the control room is 1,000 times lower than that seen in the operating room. During robotic navigation procedures utilizing Stereotaxis systems, physicians perform the ablation procedure from the control room, seated, unscrubbed, and protected.
“One of the primary benefits of the Stereotaxis system is reduction of harmful radiation to physicians, staff, and patients,” commented Sabine Ernst, co-author of the EHRA consensus statement. “The EHRA consensus statement, which was derived from evidence-based data from the literature, recognizes the Niobe remote navigation system for its contribution to making the electrophysiology lab safer by reducing radiation.”
The EHRA consensus paper adds to the list of clinical publications that have documented the significant risk of radiation exposure for physicians that perform interventional procedures. A study on interventional physicians with brain tumors found that 85 percent of tumors were in the left side of the brain as opposed to the right side, as the physicians usually stand with their left side closer to the X-ray source. It has also been reported that occupational radiation increased the risk for physician and cath lab workers for skin lesions, cataracts and cancer.
The most common method used by healthcare professionals to protect against radiation exposure while in the electrophysiology lab is the wearing of lead aprons and protective gear. Protective lead aprons may weigh over 20 pounds, and the long-term burden of this weight can lead to significant orthopedic problems. A recent survey was published that reported 49 percent of interventional cardiologists have suffered one or more orthopedic injuries as a direct result of their work in the cath lab, with 9 percent taking a health-related leave of absence.
Stereotaxis’ technology not only protects physicians and healthcare professionals from radiation exposure by removing them from the operating room, but has been shown to allow for reduced X-ray usage and associated radiation exposure for patients. While the EHRA consensus document focused on radiation exposure for healthcare professionals in the electrophysiology laboratory, the document also estimated that a patient undergoing a cardiac ablation procedure is exposed to 15.2 mSv of radiation per procedure. This value is the equivalent to approximately 760 standard chest X-rays (1 mSv = 50 chest X-rays). In an internal systematic review of peer-reviewed publications describing clinical experience with Stereotaxis’ remote magnetic navigation compared to manual ablation, comprising 20 publications and 4,567 patients in total, there was an average of 31 percent reduction in fluoroscopy time in robotic ablation procedures compared to manual ablation procedures. Stereotaxis continues to explore ways to advance its technology to allow even further reductions in radiation exposure for patients.
For more information: www.stereotaxis.com

 November 14, 2025
November 14, 2025