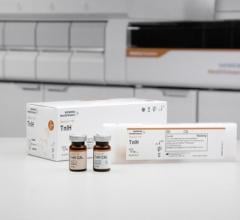
January 29, 2013 — An estimated 17 million people throughout the world die annually of cardiovascular diseases, specifically heart attacks or strokes.[1] Time is a critical factor in diagnosing and treating people who may be having a potential heart attack. To aid physicians in detecting heart attacks sooner, Abbott announced CE marking (Conformite Europeenne) for the Architect Stat High Sensitive Troponin-I Assay.
Diagnosing Potential Heart Attacks
The preferred biomarker used to identify suspected heart attacks is cardiac troponin, a protein found in the heart muscle, because it can detect injury to the heart.[2] Many patients who visit the emergency room with chest pain complaints and a suspected heart attack currently have blood samples drawn for troponin tests upon admission, after 6 hours, and then potentially 12 hours later before a diagnosis may be made.[3] For patients who are having a heart attack, the length of time to diagnosis is a crucial factor because the heart muscle cells start to die after the heart stops receiving blood, and eventually, almost all the affected parts of the heart could be irreversibly damaged.
Abbott's new Architect Stat High Sensitive Troponin-I Assay can measure very low levels of the protein, which allows doctors to evaluate whether or not patients are having a heart attack within two to four hours.[4] This faster evaluation could allow doctors to reduce the time to diagnosis and treatment by several hours when compared to standard troponin tests.
"The advantage of high sensitive troponin tests compared to current tests is that clinicians may now more precisely confirm or exclude a heart attack much sooner and with higher accuracy compared to contemporary tests," said Professor Stefan Blankenberg, director of cardiology at the University Heart Center of Hamburg, Germany. "This is important information for patient care because we can pursue treatment if needed or avoid invasive therapy and discharge a patient earlier."
Determining Risk for Future Cardiovascular Events
Another concern for patients who have experienced symptoms of a heart attack or who suffered from an actual attack is that they are at a higher risk for experiencing a second cardiac event or heart attack within a few weeks or months. Abbott's High Sensitive Troponin-I Assay also enables doctors to determine if patients are at risk to suffer from cardiovascular events 30 days and 90 days later.
"The sooner a patient can be diagnosed with a cardiac event, the faster a patient can get the care he or she needs," said Brian Blaser, executive vice president, Diagnostics Products, Abbott. "Abbott's new high sensitive troponin test is an innovative tool to help physicians diagnose more quickly, potentially improving the way heart attacks are diagnosed for patients around the world."
The new assay runs on Abbott's fully-automated Achitect family of analyzers and is available in CE marked and non-regulated countries, pending country registration.
Intended Use
The Architect Stat High Sensitive Troponin-I assay is a chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay (CMIA) for the quantitative determination of cardiac troponin I (cTnI) in human plasma and serum on the Architect i System with STAT protocol capability. The cTnI values are used as an aid in the diagnosis of myocardial infarction (MI) and to aid in the assessment of 30-day and 90-day prognosis relative to all-cause mortality and major adverse cardiac events (MACE) consisting of myocardial infarction, revascularization, and cardiac death in patients who present with symptoms suggestive of acute coronary syndrome (ACS).
For more information: www.abbott.com
References:
1. Cardiovascular Diseases Fact Sheet No 317. World Health Organization, September 2012. Web site:www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs317.
2. Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS et al. Third universal definition of myocardial infarction. European Heart Journal. 2012; 33:2551-2567.
3. Thygesen K, Alpert JS, White HD et al. Universal definition of myocardial infarction. European Heart Journal. 2007; 28:2525-38.
4. Abbott ARCHITECT STAT High Sensitive Troponin-I Product Insert (PI), January 2013.
5. Cardiovascular Diseases Fact Sheet No 317. World Health Organization, September 2012. Web site:www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs317.


 October 09, 2019
October 09, 2019