Artificial intelligence in medical imaging was the major buzz at RSNA 2018. The expo floor had a dedicated area just to highlight artificial intelligence software for medical imaging. More than 150 vendors on the expo floor were showing software using some level of AI or deep learning.
Artificial intelligence (AI) was by far the hottest trend discussed in sessions and across the expo floor at the world's largest radiology conference, the 2018 Radiological Society Of North America (RSNA). At the meeting in late November, there was an explosion of AI and deep learning algorithms across the expo floor. How machine learning will impact medical imaging was the key takeaway from the opening session, where examples of how AI will alter medical imaging in the near future were highlighted. Here is an overview of the types of AI software being developed and a few examples from RSNA that are specific to cardiovascular imaging.
How Artificial Intelligence Will Impact Cardiovascular Care
Artificial intelligence has been a growing topic in past years at RSNA, but this year several companies showed products that recently gained U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) market clearance. Many more were shown as works in progress (WIP) or are pending FDA review.
There are four main areas where AI is being implemented:
1. Computer-aided diagnosis
2. Clinical decision support
3. Quantitative analysis tools
4. Computer-aided detection
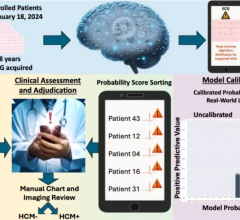
Automated quantification tools are entering a level of maturity and acceptance in the market, with AI making measurements from imaging exams and autofilling fields or performing calculations that were previously manual and time-consuming. This technology runs in the background of numerous products already in clinical use, including most of the premium echocardiography system.
AI-driven quantitative analysis tools also are being used in data analytics software for departmental and hospital business management. Rather than the old and cumbersome process of running Crystal reports or manually tabulating data points, AI software can datamine connected electronic medical records, billing systems, patient scheduling and even individual scanning equipment. This data can be mined for everything from the amount of X-ray dose used by specific technologists or computed tomography (CT) scanner in specific exam protocols, to predictive analytics software that can pinpoint the dates and times there were be backups in the department and additional staff should be scheduled.
The newer AI areas of computer-aided diagnosis and clinical decision support were only recently introduced into the market and may take several years before they are found in general use. The primary areas where AI image diagnostic software is being developed and commercialized is for critical findings such as stroke where timing is crucial. Other areas include identification of incidental findings and tools to reduce the time it takes to review complex exams like cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). AI is also being developed to help auto triage patients who need additional or more immediate care.
Computer-aided detection has been around for years, but with the addition of machine learning algorithms, experts in the field are calling the newer generation AI-supported software “CAD that works” because of its much lower rate of false positives.
Below are some examples of relevant AI at RSNA.
AI Predicts Cardiovascular Disease Risk From CT Scans
Zebra Medical Vision and Clalit Health Services presented a research project that allows early identification of patients with cardiovascular disease using AI. Using existing computed tomography (CT) data, Zebra-Med’s AI algorithms allow Clalit to identify patients at risk of cardiac events.
Clalit operates 1,500 primary care clinics and 14 hospitals, including 30 percent of Israel’s hospital acute care beds, treating over 4 million patients.
A five-year retrospective cohort study of 14,135 patients with non-gated, unenhanced chest CT was used to examine the cardiovascular predictive power of Zebra-Med’s automatic coronary calcium scoring (CCS) algorithm. Prediction performance results were compared between the American Heart Association (AHA) 2013 predictive model (base model) and the same model with the Zebra-Med CCS inserted as an additional predictor (augmented model). The addition of Zebra-Med’s CCS improved sensitivity and specificity of the contemporary gold-standard AHA model, resulting in a net 4.5 percent categorical risk-reclassification improvement.
AI Automates Ejection Fraction Analysis on Handheld Ultrasound
DiA Imaging Analysis showed its FDA-cleared LVivo EF cardiac decision-support software, which is now offered on GE Healthcare's Vscan Extend handheld, pocket-sized ultrasound. LVivo EF is the first AI-powered, ejection fraction (EF) automated app able to operate in the low-memory and processing-power environments of mobile ultrasound. Traditionally, most EF interpretation at point of care is conducted through visual estimation, with clinician experience levels varying across point-of-care settings. The software uses advanced pattern recognition algorithms that imitate the way the human eye identifies borders and motion.
Artificial Intelligence Automates, Speeds Cardiac MRI
HeartVista demonstrated an AI-driven, one-click autonomous MRI acquisition software for cardiac exams. The FDA-pending software can be integrated with existing MRI scanners, and the software uses AI to guide image acquisition. The company said a single click enables a technologist to perform a cardiac ischemia exam in less than 15 minutes, compared to the traditional 90-minute session.
HeartVista's software automatically prescribes the standard cardiac views in as little as 10 seconds while the patient breathes freely. An artifact detection algorithm is incorporated in HeartVista's autonomous protocol to detect when the image quality is below the acceptable range, prompting the operator to reacquire the questioned images if desired. An accelerated non-Cartesian 4-D flow sequence is acquired in minutes, leaving enough time for the necessary calibrations prior to the myocardial delayed-enhancement acquisition. The smart in-line cardiac analysis package provides preliminary measurements of left ventricular function.
The company said the software may remove barriers for wider adoption of cardiac MRI. Patients may benefit from fewer breath holds and reduced discomfort. Technologists benefit from the reduced complexity of exams.
HeartVista is partnering with Siemens and NVIDIA.
Arterys demonstrated deep learning, cloud-based image analysis solutions for cardiac MRI. Its Cardio AIMR automates analysis and eliminates many tedious, manual tasks, Arterys Cardio AI enables clinicians to quickly and easily identify, determine treatment for and track heart problems. It is the only commercial solution, according to the company, to offer deep learning-based semi-quantitative perfusion and quantitative delayed enhancement analysis.
Another example of AI-assisted MRI automation software was CoreStem, which takes a cardiac MRI dataset and automatically segments the anatomy as well as performs functional quantification measurements. The reviewing radiologist can change the AI contouring and the system will automatically calculate the measurements. This software was shown in the TeraRecon booth as one of numerous AI-based apps offered through the vendor’s Envoy AI App Store, which amalgamates startup company AI apps in one location from a single vendor.
AI CT Image Reconstruction Algorithm
The Canon Aquilion Precision CT system gained FDA clearance in 2018 and offers a resolution of 0.25 mm to enable visualization of fine details not seen on most of the current-generation CT systems. However, the better resolution comes at a higher cost in dose, so to reduce the dose back down to the level of a conventional scan, Canon developed a smart algorithm called the Advanced Intelligent Clear-IQ Engine (AiCE). It uses deep learning to tell the difference between noise and signal, and the AiCE algorithm “learns” to improve the resolution of CT images. It reconstructs CT images from the high-quality images produced using model-based iterative reconstruction (MBIR). The technology is being deployed on the Precision CT system first and will be rolled out to other system in the future.
Another example of AI for CT was demonstrated by Philips Healthcare, which designed an algorithm to automatically identify anatomical structures around and inside the heart and color code them without human intervention. The goal is to speed workflow significantly instead of using a technologist to spend a large amount of time to perform the same task.
AI to Immediately Diagnose Hemorrhagic or Ischemic Strokes
There is fear in radiology that AI may take people's jobs in the future, so there is a lot of apprehension about the technology. However, in the areas of emergency care where immediate information is needed to treat a patient, AI is viewed differently because of its potential to offer insights scanner side in the emergency department before a radiologist even has a chance to look at it, especially in smaller and remote hospitals where immediate access to a neuro specialist might be limited. In the case of stroke, time is brain, tPA needs to be administrated as soon as possible within a 90 minute window after a stroke. However, a CT scan needs to be determined if a patient is having a stroke and then what type it is, hemorrhagic or ischemic. The use of tPA in a hemorrhagic case could have catastrophic consequences for the patient, so immediate identification of the type of stroke is crucial. This is why some of the first FDA-cleared AI algorithms to actually diagnose a patient are in the area of stroke.
MaxQ AI's FDA-cleared Accipio Ix software leverages AI to automatically analyze non-contrast head CT images. It is designed to be highly sensitive to the presence of intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH), identifying and prioritizing patients with a brain bleed for the treating physician. It provides a capability for rapid escalation and prioritization of the patient and can be natively integrated into CT and picture archiving and communication systems (PACS) and can be installed both on-premise and as a cloud app.
Watch a couple short examples of the Accipio AI in the VIDEO: How Artificial Intelligence Can Detect Brain Bleeds.
At RSNA, Samsung NeuroLogica announced a distribution agreement with MaxQ AI, integrating Accipio Ix into NeuroLogica’s medical imaging platforms in the U.S. and Europe, including the OmniTom mobile 16-slice CT scanner. In addition, MaxQ’s AI solutions will be available for integration into Samsung NeuroLogica’s U.S. and EU mobile stroke units (MSU), a specialized ambulance or other emergency vehicle that is equipped with a CereTom CT scanner.
Viz.AI also offers an FDA-cleared software that can identify ischemic strokes from CT scans. The software then sends an automated alert to the neuro expert on call for an immediate review of the images on their smartphone. It also performs auto quantification.
Related AI Content From RSNA 2018:
Technology Report: Artificial Intelligence at RSNA 2018
VIDEO: RSNA Post-game Report on Artificial Intelligence — Overview report with editors Dave Fornell and Greg Freiherr
VIDEO: AI, Analytics and Informatics: The Future is Here — Interview with RSNA 2018 keynote speaker Michael Recht, M.D.
VIDEO: RSNA President Vijay Rao Says Artificial Intelligence is Hottest Tech at RSNA 2018
VIDEO: Artificial Intelligence May Help Reduce Gadolinium Dose in MRI — interview with
Enhao Gong, Ph.D.
VIDEO: A Tour of the Artificial Intelligence Showcase at RSNA 2018
VIDEO: AI in Tumor Diagnostics, Treatment and Follow-up — Interview with Julius Chapiro, M.D.
VIDEO: Example of How Artificial Intelligence Can Improve Patient Care


 September 24, 2025
September 24, 2025