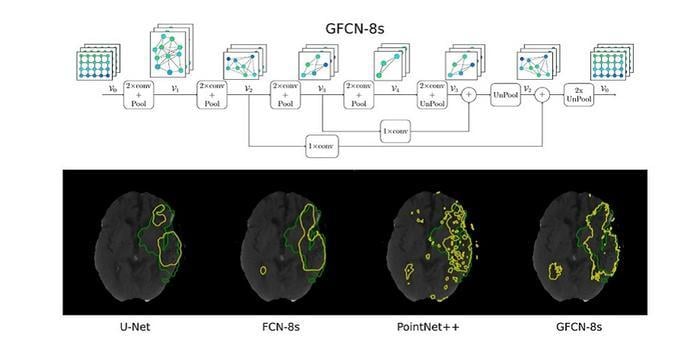
GFCN-8s, the proposed geometric deep learning network with three pooling layers and eight-fold upsampling, can extract rich geometric information from computed tomography scans of the brain. This enables it to outperform the state-of-the-art models (U-Net, FCN-8s, and PointNet++) in detecting stroke lesions. Iporre-Rivas et al., doi 10.1117/1.JMI.10.4.044502.
July 19, 2023 — Ischemic stroke, which occurs when a blood vessel in the brain gets blocked by a clot, is among the leading causes of death worldwide. Fortunately, surgeons now have access to advanced imaging techniques that allow them to visualize the interior of a patient’s brain during a stroke. This helps them pinpoint the location of the clot and analyze the extent of damage to the brain tissue.
Computed tomography-perfusion (CT-P) is one of the most useful imaging modalities in the early stages of an acute stroke. However, it is challenging to accurately identify segmentation—the outline of stroke lesions—in a CT-P scan, and the final diagnosis depends greatly on the surgeon’s expertise and ability. To address this issue, scientists have come up with various machine learning models that perform automatic segmentation of CT-P scans. Unfortunately, none of them has reached a level of performance suitable for clinical applications.
Against this backdrop, a team of researchers from Germany recently developed a new segmentation algorithm for stroke lesions. As reported in their study published in the Journal of Medical Imaging, the team built a geometric deep learning model called “Graph Fully-Convolutional Network” (GFCN). The internal operations performed by their geometric algorithm differ fundamentally from those of the more widely used Euclidean models. In their study, the researchers explored the benefits and limitations of this alternative approach.
A key advantage of the proposed model is that it can better learn and preserve important features inherent to brain topology. By using a graph-based neural network, the algorithm can detect complex inter-pixel relationships from different angles. This, in turn, enables it to detect stroke lesions more accurately.
In addition, the team adopted “pooling” and “unpooling” blocks in their network structure. Put simply, the pooling operations, also called “downsampling,” reduce the overall size of the feature maps extracted by the network from input images. This reduces the computational complexity of the algorithm, enabling the model to extract the most salient features of the CT-P scans. In contrast, the unpooling operations (or “upsampling”) revert the pooling operations to help properly localize the detected features in the original image based on contextual cues. By combining these two operations, the network structure can extract richer geometric information.
The team conducted a series of analyses to determine the effect of each component of GFCN on its segmentation performance. They then compared the performance of the proposed algorithm against the state-of-the-art models, all trained using the same public dataset. Interestingly, although their model used basic unpooling techniques and a simple input configuration, it performed better than the conventional models under most conditions.
Notably, GFCN-8s, with three pooling layers and eight-fold upsampling, achieved a Dice coefficient score—a metric indicating the overlap between the predicted and actual lesion areas—of 0.4553, which is significantly higher than other models. Moreover, the proposed model could adapt to irregular segmentation boundaries better than the state-of-the-art models.
Overall, the findings of this study showcase the potential of geometric deep learning for segmentation problems in medical imaging. Further research on similar strategies could pave the way for highly accurate models for automatic stroke diagnosis that could improve patient outcomes and save lives.
Read the Gold Open Access article by A. Iporre-Rivas et al., “Stroke-GFCN: ischemic stroke lesion prediction with a fully convolutional graph network,” J. Med. Imag. 10(4) 044502 (2023), doi 10.1117/1.JMI.10.4.044502.
For more information: https://spie.org

 January 28, 2026
January 28, 2026