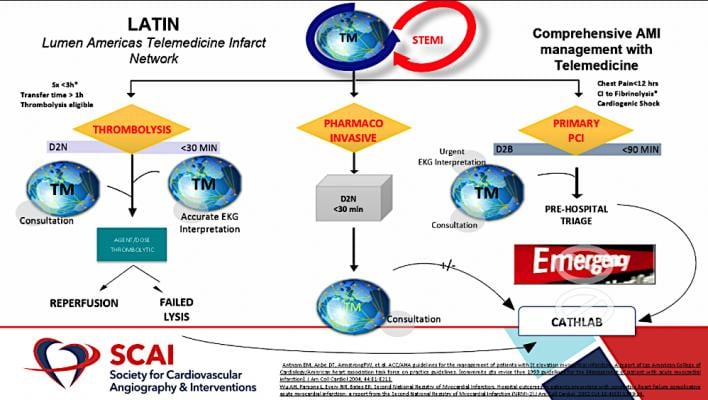
The protocol chart for the LATIN STEMI telecardiology program.
May 15, 2020 – A groundbreaking trial recently examined the viability of telemedicine for remote guidance of a population-based ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) program reaching more than 100 million patients. The study, presented as late-breaking science during the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI) 2020 Virtual Conference.
The study helps further prove that telecardiology transcends boundaries, enabling millions of patients to have STEMI care access.
Telemedicine allows healthcare professionals to evaluate, diagnose and treat patients at a distance using telecommunications technology. Within the last decade, the approach has seen striking evolution and in the current COVID-19 climate, has become increasingly important to ensure patients have access to the care they need.
During the study, patients were triaged at spokes that included small clinics and primary healthcare centers in remote locations and transferred to hubs with percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)-capability. The Latin America Telemedicine Network (LATIN) functioned between 2013 to present in four countries – Brazil, Colombia, Mexico and Argentina.
"As Americans see the benefits of telemedicine in the COVID-19 era, the findings of the [LATIN investigation] should be more relevant and noteworthy,” said Sameer Mehta, M.D., lead author and chairman of the Lumen Foundation. “LATIN is the result of dedicated efforts of more than 2,000 healthcare professionals, including about 600 physicians that were involved in this decade old program.”
Almost 900,000 patients presenting at 351 remote locations were triaged through a STEMI network. The program provided an umbrella of AMI protection to more than 100 million patients in Brazil, Colombia, Mexico, and Argentina. Mortality was reduced by 55 percent and the program contributed to saving $291 million. The results from LATIN trial surpass the total accumulated global experience with telemedicine.
The study investigators tested and proved four attributes of telemedicine:
• Increased access • Increased accuracy.
• Cost-effectiveness.
• Comprehensive, population-based care and delivery of guidelines-based acute myocardial infarction (AMI) management.
The program was created as a hub and spoke model that was used to expand access. Patients presented at remote clinics and primary care centers and were guided through telemedicine to receive thrombolysis, pharmaco-invasive management, or primary PCI. The role of the telemedicine experts was two-fold: urgent and accurate STEMI diagnosis and tele consultation of the entire STEMI process. Time to telemedicine diagnosis (TTD) was 3.5 minutes and it was possible from tremendous investment in IT infrastructure, with use of cloud computing, business intelligence tools and with GPS navigation. LATIN established TTD as a novel metric of telemedicine efficiency.
“LATIN has established the role of telemedicine in cost-effective and population-based management of AMI that reduces disparities of AMI care between developed and developing countries,” said Mehta. “It has provided a template that can be most beneficial for poorer regions on the world, including in sub-Saharan Africa, the Middle East and in southeast Asia. LATIN can also serve as a model of providing population-based coverage for other systems guided entities such as stroke."
Find links to the rest of the SCAI late-breaking trials and other SCAI news


 January 05, 2026
January 05, 2026 









