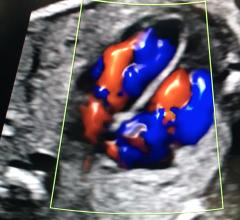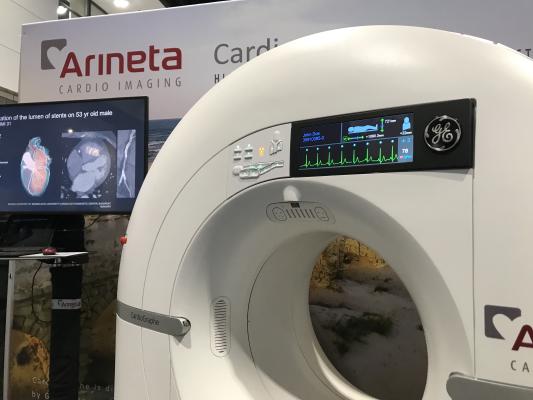
Arineta created a dedicated cardiac CT scanner in partnership with GE Healthcare several years ago. With increased interest in CTA with the new chest pain guidelines, the company decided to also start direct sales of these systems for the first time at RSNA in their own booth. Photos by Dave Fornell
Here are a few of the key takeaways on the new technologies that will impact cardiovascular and interventional medicine displayed at the 2021 Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) meeting.
1. Advances in CT Help in Cardiology
New international guidelines on how to evaluate patients with chest pain were released in October 2021, and it raised the level of evidence for using computed tomography (CT) angiography (CTA), now making CT a front line imaging mobility. This translated into interest and discussions in CT with all the major vendors. This change in guidelines is also expected to rapidly propel the use of CTA for chest pain over the next several years.
This coincided with the display of the first FDA-cleared photon counting CT system, the Siemens Naeotom Alpha, which was cleared by the FDA in late September 2021. Both FDA and CT experts say this is the start of a revolution in new CT scanner technology, and is the biggest shift in technology for this workhorse radiology modality in more than a decade.
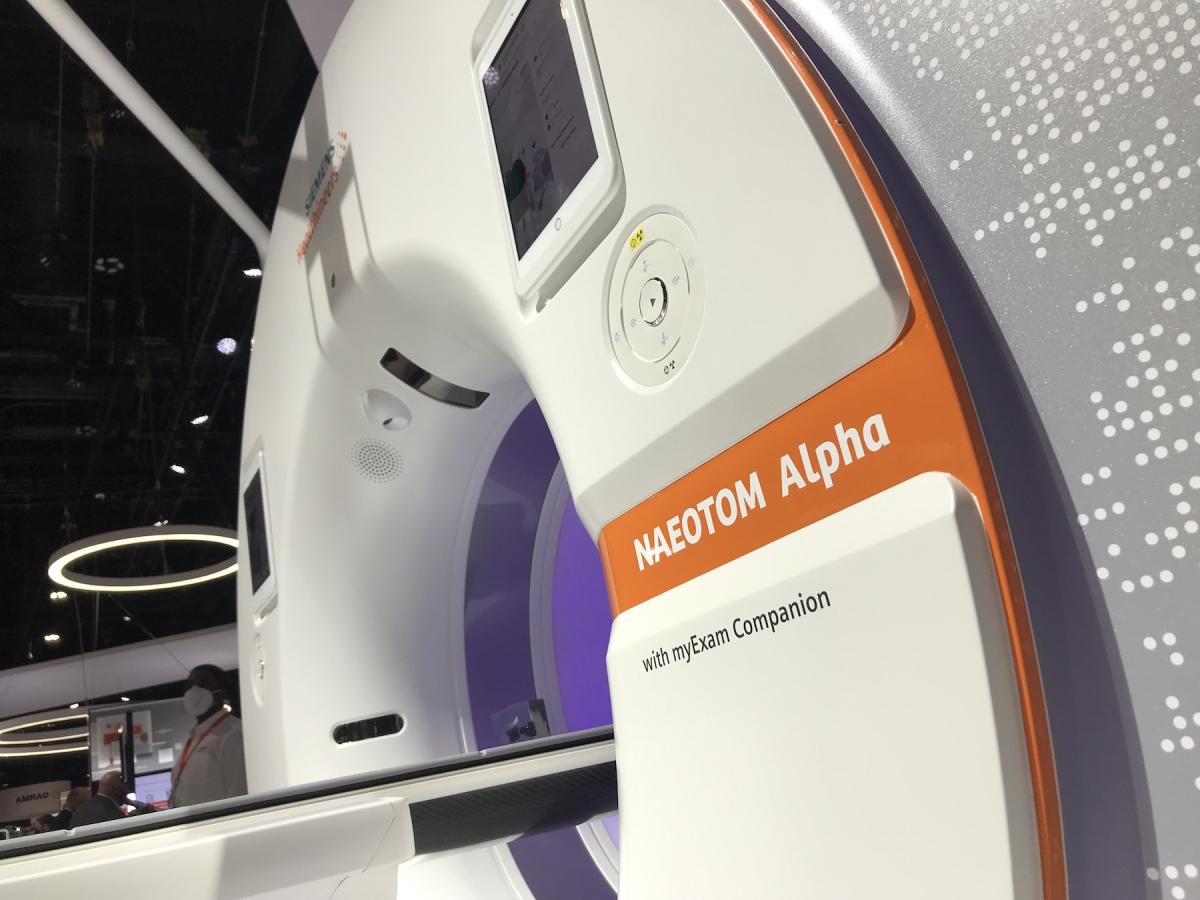

The device uses the emerging CT technology of photon-counting detectors, which can measure each individual X-ray photon that passes through a patient's body, as opposed to current systems which use detectors that measure the total energy contained in many X-rays at once. By "counting" each individual X-ray photon, more detailed information about the patient can be obtained and used to create images with less information that is not useful, such as image noise. These detectors also allow for direct conversion of emitted X-rays into energy, eliminating intermediate steps used to convert light into electrical signals on current scanners. This improves efficiency and image quality.
The higher image resolution combined with spectral imaging capability hold promise in cardiac imaging because it will enable more confidence in scanning patients who have stents or who have highly calcified coronary arteries
This system, and other photo-counting systems now in development, promise to greatly enhance CT imaging quality and resolution, and build in spectral imaging on every scan. An example of the image quality shown at several cardiology meetings is the ability to not only make out enough detail to identify a specific vendor's stent, but also to view soft plaques and restenosis inside the stent, which is very difficult with current CT technology.
Arineta created a dedicated cardiac CT scanner in partnership with GE Healthcare several years ago. With increased interest in CTA with the new chest pain guidelines, the company decided to also start direct sales of these systems for the first time at RSNA in their own booth.
The purpose-built scanner for cardiac imaging offers a very fast temporal resolution that can scan without the need for beta blockers with heartbeats into 80 beats per minute. It is being used clinically to evaluate chest pain, detailed studies of the coronaries, and structural heart procedure planning. The company also partnered with HeartFlow to offer FFR-CT analysis.
Its very small size and low weight allows it to be installed in small rooms, office-based practices or in mobile platforms such as trucks or RV chassis for mobile imaging.
The company is also offering offering the system for free, using a pay-per-study agreement. The cost of the system is well below $1 million, including the ECG gating and contrast injection systems.
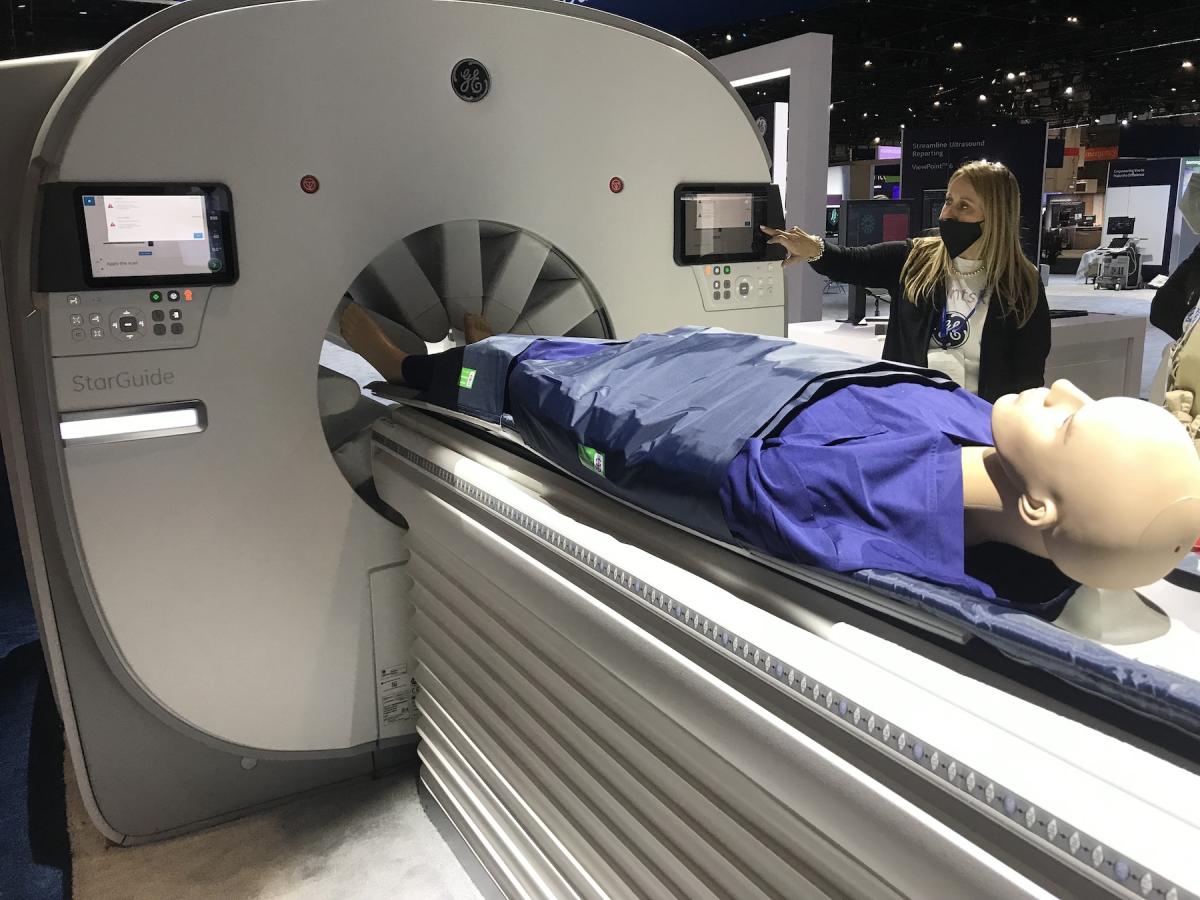
GE Healthcare showed its new StarGuide SPECT-CT scanner for the first time at RSNA 2021. The nuclear scanner has a series of cadmium zinc telluride (CZT) direct conversion detectors mounted on extendable arms. These arms move into the imaging bore to get as close as possible to the patient to optimize image quality. This also allows the detector to focus on the anatomy of interest, such as the heart. The system has both CE mark and FDA clearance.
2. Advances in MRI May Enable More Patients With Implantable Devices to be Imaged
Siemens showed its Magnatom Free.Max magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system for the first time at RSNA. It was cleared by the FDA in July 2021. It has a lower magnetic field and uses an algorithm that enables imaging more patients with implantable cardiac devices.
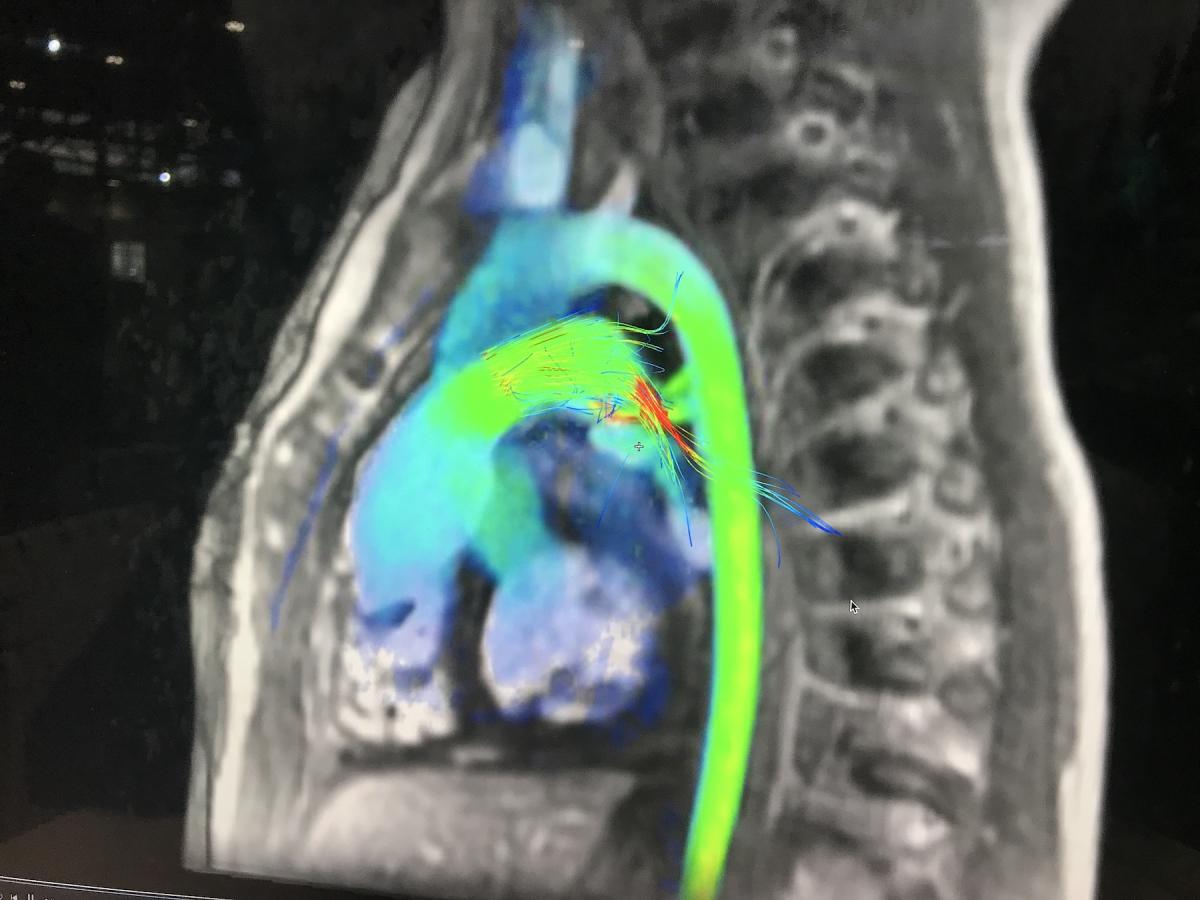
The system offers a an 80 cm bore to accommodate larger patients and reduce claustrophobia. It also features a sealed system that uses only 0.7 liters of helium and prevents boil off. This can reduce the costs of maintaining the system. It also uses deep-learning algorithms to shorten scan times and improve image quality.
Several vendors at RSNA also showed new technologies to reduce the complexity of MRI protocol set up, decrease scan times, and use artificial intelligence (AI) to automatically analyze and create measurements on cardiac MRI scans. These features are expected by some experts in the field to increase access to MRI by allowing more patients to be scanned per day, and make cardiac MRI easier and less time consuming to perform.
3. New Cath Lab Radiation Protection Systems
Two cath lab radiation protection systems displayed at RSNA for the first time gained a lot of interest from interventional cardiologists and radiologists.
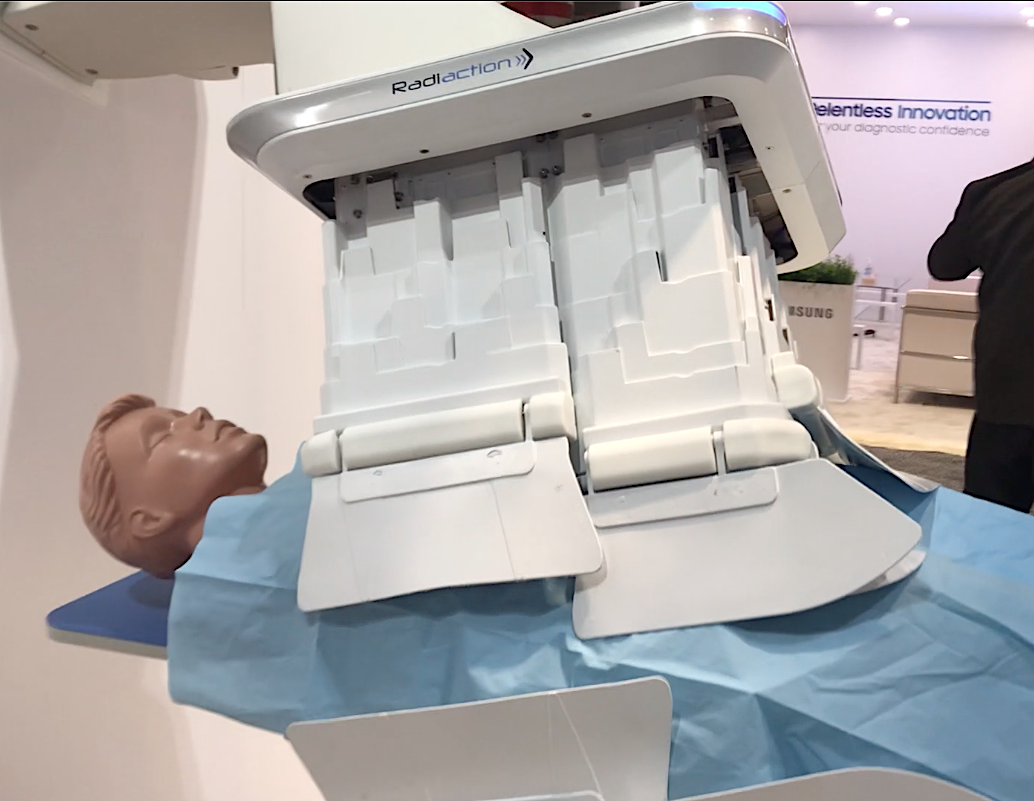
The Radiaction Shield System to prevent scatter radiation in the cath lab fits an expanding shield to the detector and X-ray source on the C-arm. The light weight shield is made of leaves of tungsten mixed into a polymer. It can be deployed using a table-side controller. It extends down from all four sides of the detector and moves down to the patient until sensors detect their proximity (or that of a hand or piece of equipment) and stop automatically. When pulled back, the shield folds compactly into itself and out of the way to allow normal access space between the patient and the C-arm.
The vendor said it can lower scatter radiation dose in the cath lab by 97%, and is gathering more study data to show safety and the reduction in staff exposure during procedures.
The company has CE mark and is submitting for FDA in 2022. Two sites in Israel are using the system clinically.
Watch a VIDEO demonstration of this system on the RSNA show floor
Another technology that garnered a lot of interest was a weightless lead protection apron for use by interventionalists in the cath lab made by the Taiwanese vendor Becquerel & Sievert Co., Ltd. It offers more radiation protection than traditional lead aprons, and the weight is supported by a steel tube frame that is on wheels so the operator can move around the room.
4. Improved Interventional Guidance and Imaging
Siemens did not show an angiography system at RSNA this year, but did exhibit its cath lab robotic Corindus Corpath catheter guidance system at this conference for the first time. Attendees could try using the system to navigate catheters through vessels for simulated coronary or vascular interventional procedures. Siemens wanted to show other aspects of its image-guided interventional offerings beyond the imaging systems.
The Corpath system enables the interventional operator to manipulate catheters from a lead-lined cockpit inside the cath lab, seated, and without the need to wear lead protective aprons. The system removes the operator from the radiation field to improve their safety, and significantly reducing their exposure to scatter radiation. The system is said to offer more control of the catheter and its navigation over traditional manual manipulation of the catheters. The vendor says this can help increase accuracy in the procedures and lead to better patient outcomes. Users of the system said it offers advantages during longer and more complex procedures.
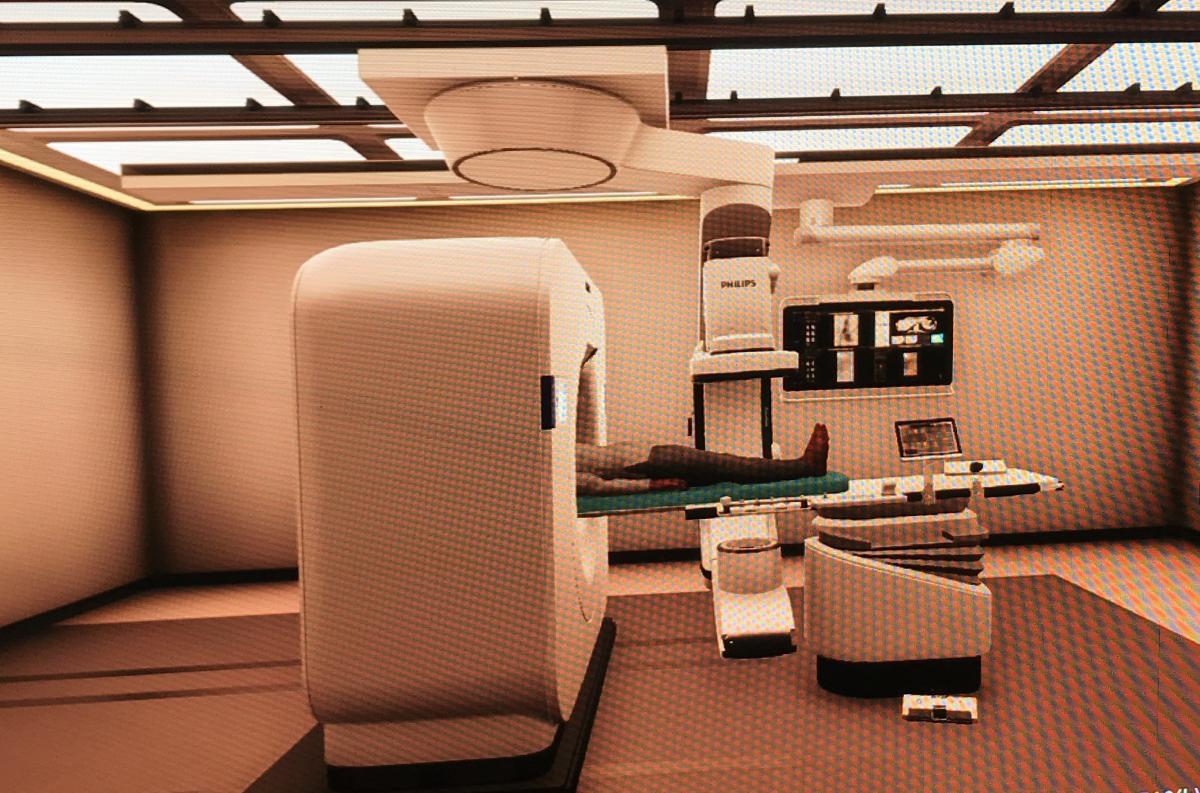

Philips introduced a new combined angiography-CT imaging system for the cath lab that is currently FDA 510(k) pending. It is designed to better guide procedures and verify results on CT prior to patients leaving the cath lab. The system was co-developed with Mayo Clinic to incorporate an Azurion angiography system and a CT scanner in the same room for immediate CT imaging of the quality of ablation lesions or success of interventional radiology embolization procedures, which can be checked while the patient is still on the table.
The 256-slice 7500 series CT system was modified to change the isocenter to accommodate the angiography system's patient table inside the CT bore. The CT has 8 cm of anatomical coverage in one rotation and a high temporal rotation speed of 0.27 seconds, so patients with heartbeats up to 75 BPM can be images. The scanner uses a dual-layer detector that absorbs different kV energies, so it has built-in spectral imaging capability on all scans.
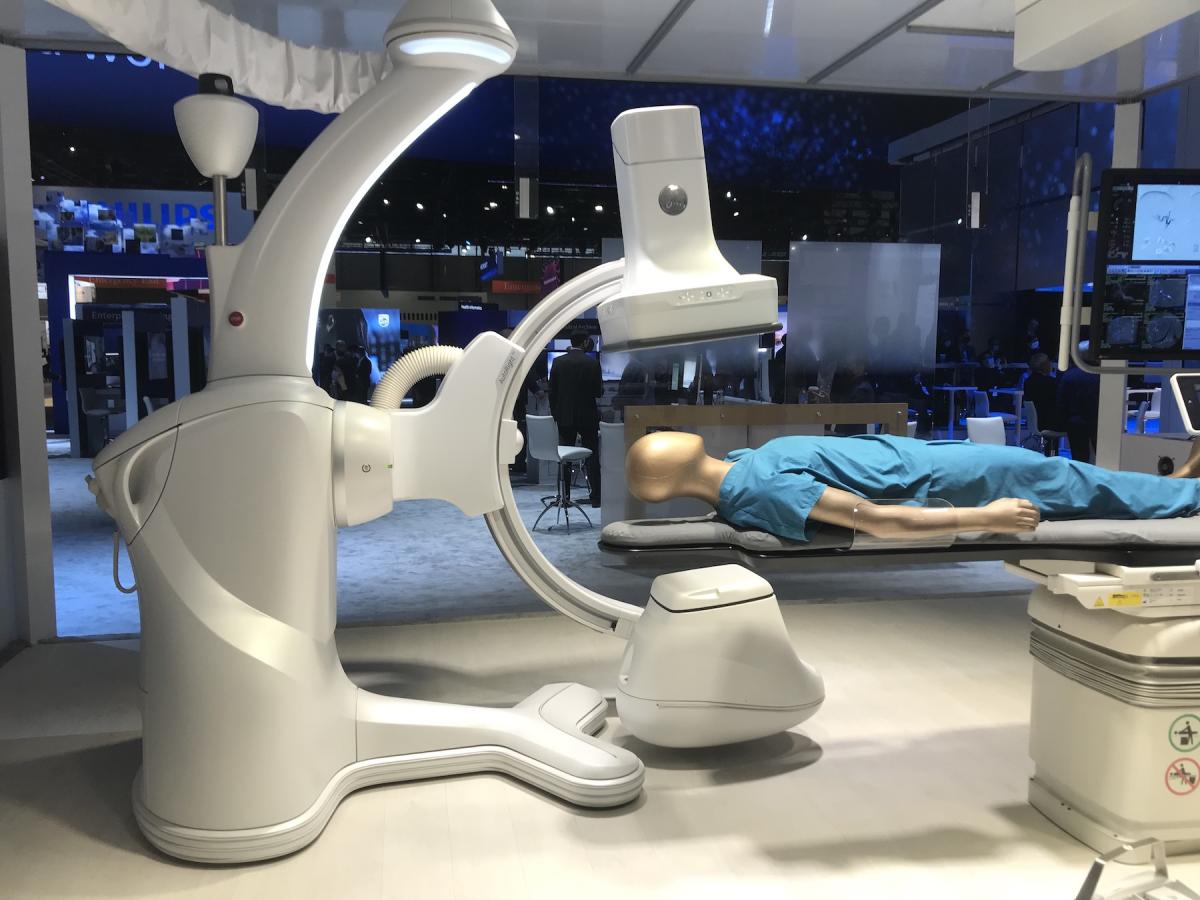
GE Healthcare showed its new Allia IGS7 angiography system. It was released in 2020 and the first system is now being installed. It features an all new user interface with a set of controls duplicated on three sides of the detector head. A set of controls for the system are also available on a small cart, a taking up the same amount of floor space as an IV stand so the C-arm can be operated from anywhere in the lab.
The IGS platform is neither floor or ceiling mounted like conventional systems. It uses a robotic gantry system that can roll around the room, using lasers to pin point here the system is loaded in the room and in relation to the patient table. It can be parked in a corner of the room to allow easier patient access.
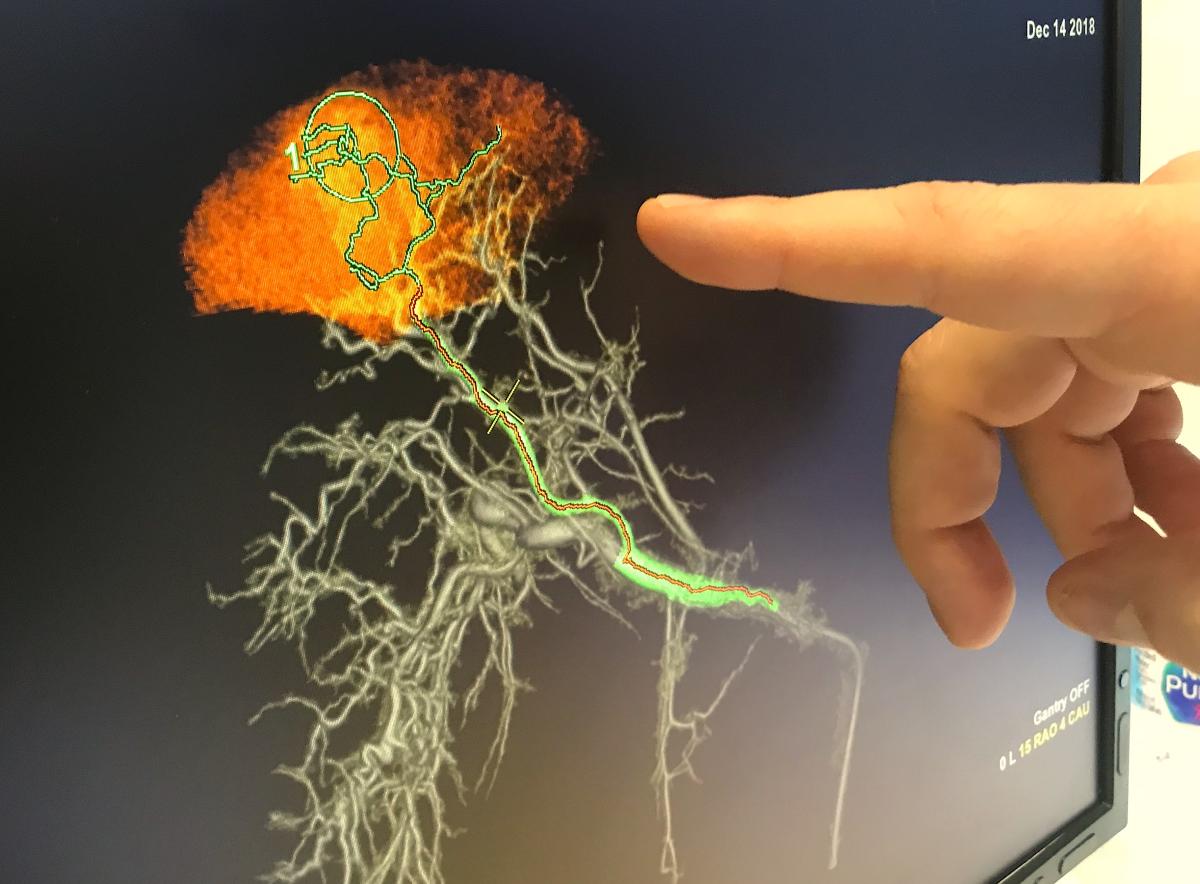
For the interventional radiology market, GE also showed a new version of its Liver Assist vascular embolization guidance technology. The software uses a sweep of the C-arm to create a 3D anatomical model of the liver and vasculature. It then shows center lines for the various access routes to a target lesion to be mobilized. The new version of the software offers AI-enabled Virtual Parenchyma, which predicts the tissues that will be effected by an embolization in various vessels to aid with procedure planning prior to the actual embolization.
5. AI For Vascular Intervention Teams
Artificial intelligence has found a unique niche to help automate the activation of acute care teams for pulmonary embolism (PE), aortic dissections and abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA) and allow them access to imaging and immediate communications. This concept was highlighted for stroke response teams at RSNA 2019 and AI vendors this year are rapidly moving into other areas where there is a need for fast acute care team activation. This was one of the key AI takeaway trends at this year's meeting.
Read more about this technology at RSNA 2021
6. Consolidating Imaging and Data Through Enterprise Imaging Improves Efficiency
Web-based enterprise imaging systems were a major trend at RSNA on the health IT side of things. These systems simplify several issues with older departmental IT systems, where data and imaging are often siloed and unable to be accessed outside the department or by the EMR. Hospitals often have separate reporting systems, image storage and data storage systems for every department, which also complicates things and does not enable access to all of a patient's information in one location.
Enterprise imaging systems overcome this by using a central data repository, a vendor neutral archive (VNA), where all the data from the hospital can be stored in one large, easily accessible container. This enables cardiology images and reports to be accessible to anyone in the hospital who may need them without the need for different longing or decimated workstations. Web-based systems also allow access to this information anywhere, including on tables and other mobile devices, so clinicians are no longer tethered to a workstation computer.
Trends in enterprise imaging at RSNA include a movement to large data storage providers such as Google and Amazon. Many hospitals have come to the realization these larger IT companies offer far more security and ease to scale up than their own IT departments can provide. As health systems move to enterprise imaging platforms, these vendors also can help them enable access to all the clinicians across their enterprise in all departments access to a complete picture of a patient's history and imaging in one place with minimal involvement from their own IT department.
IT is also being integrated into seamless workflows on the backend by enterprise imaging vendors, rather than offering AI apps as a separate software that sits on top of the reporting systems or require separate logins and may not share discreet data fields needed in reports.
Structured reporting, zero-footprint image viewers and the ability to customize workflows and report templates at the hospital department level were also shown by multiple vendors.
Another key trend in enterprise imaging systems is the use of AI-enabled workflow orchestration software. This can save a lot of time and pain points with workflow optimization, load balancing various types of studies read by a team of radiologists, automating position of studies to read in wordlists based on service level agreements (SLAs), and to capture data on all aspects the patients, users of the system, types of studies and reports in the system, etc.
Change Healthcare demonstrated how structured reporting can be integrated into CVIS to enhance data collection and later data mining and analytics review. The vendor also showed how a newer web-native enterprise system can leverage a zero-footprint workflow, where all the data, images and software reside on the web, not on the local server or computer. The system also enables users to build their own customized reports and workflow, since these can differ greatly from health system to health system.
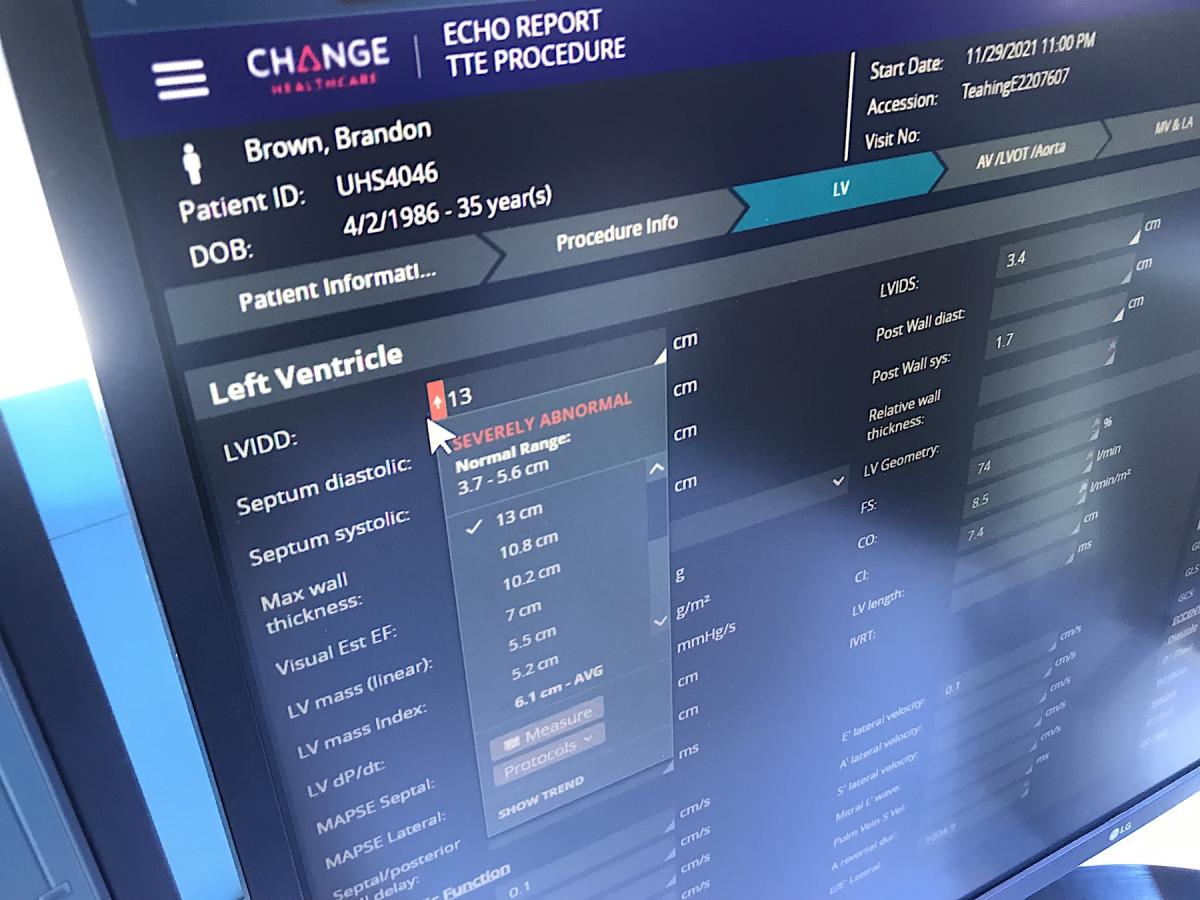
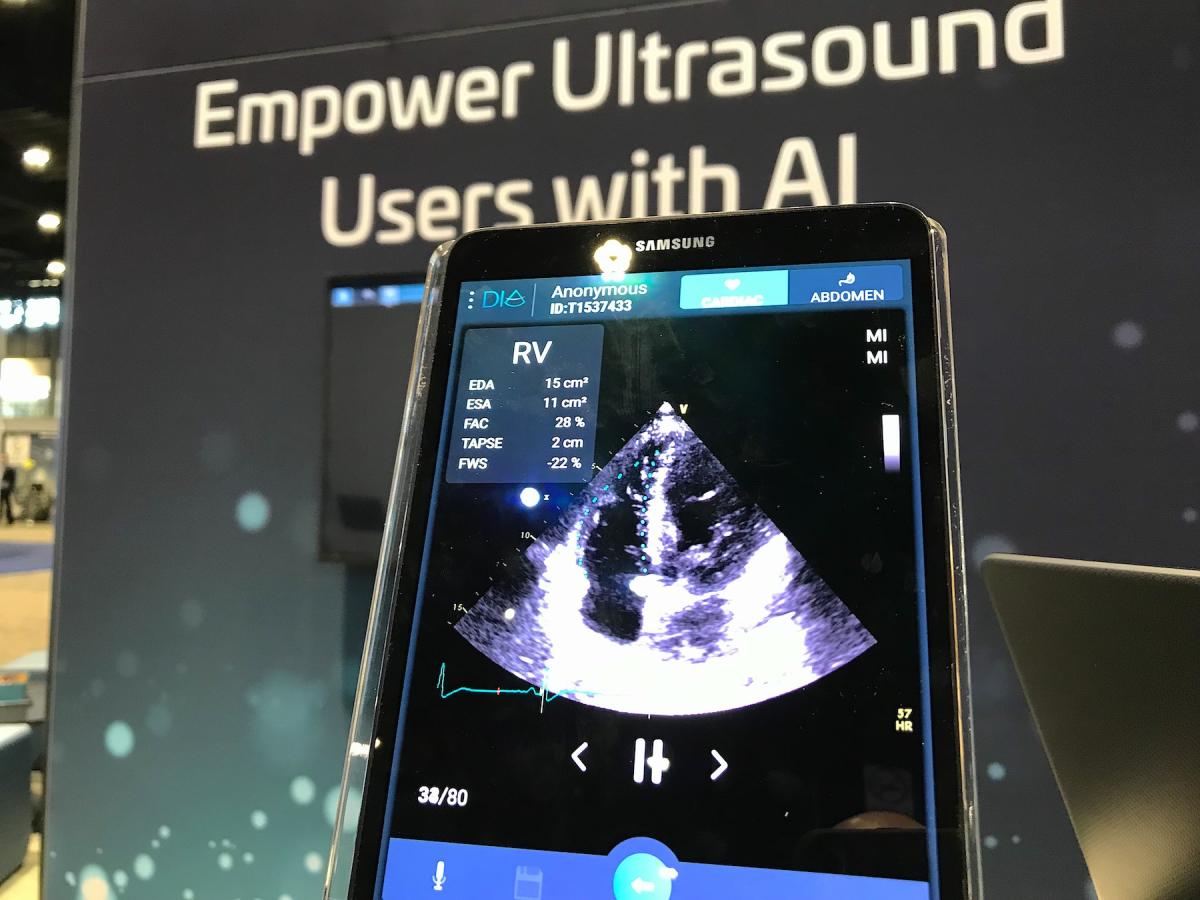
Change is working with AI vendors to embed cardiology workflows into the system seamlessly. An example of this is a partnership with Dia to automate echocardiography measurements and strain. The system also will be able to identify and alert the user when automated measurements are outside the ASE guidelines. Automated text generated from the imaging will also be available to pick from in a drop down menu to speed report completion.
Another example of one of these systems is Canon's Vital enterprise imaging system. This system was adopted by Ochsner Health in Louisiana to consolidate its cardiology, radiology imaging, and create a central repository for all of its other departments that produce, images, waveforms and other data. Canon said Ochsner is using their VNA to retire more than 30 older, unconnected archives used by various departments and to simplify its storage and access to patient data and images.
Canon also has close partnerships for vascular advanced visualization software from Medis and TomTec, which is fully integrated into the system, rather that being a third-party software interface outside system. Canon is also working with some AI vendors to seamlessly embed the various AI applications for other vendors into the Vital workflow.
One interesting feature shown by NovaRad for its enterprise imaging system was printing out a small card with a QR code for a patient during their visit that can be scanned with their smartphone, or texted to a patient. It immediately takes them to their patient portal and their imaging datasets, labs, reports and other data. This can then be shared with any referring physician or another doctor for a second opinion, and eliminates the need for burning and transporting CDs. This system also addresses patient privacy and HIPAA concerns.
Photo Gallery of Cardiovascular Technology on Display at RSNA 2021


 October 08, 2025
October 08, 2025