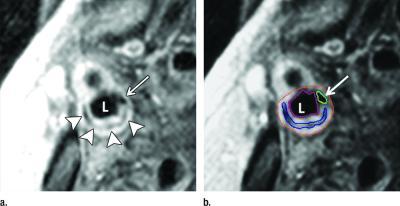
This shows transverse gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted MR images obtained superior to the carotid artery bifurcation in a 72-year-old man. L = ICA lumen. (a) Low-signal-intensity calcium (arrow) and lipid core (arrowheads) can be seen. (b) Note contouring of the ICA. The outer adventitial wall (red), lipid core (blue), calcification (green), and vessel lumen (purple) are visible.Credit: Radiological Society of North America
March 5, 2014 — Noninvasive imaging of carotid artery plaque with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can accurately predict future cardiovascular events like strokes and heart attacks in people without a history of cardiovascular disease, according to a study published online in the journal Radiology.
Researchers have long known that some arterial plaque is more dangerous because of its vulnerability to rupture. MRI can discern features of vulnerable plaque, such as a lipid core with a thin fibrous cap. This ability makes MRI a potentially valuable tool for identifying patients at risk for subsequent cardiovascular events.
To study the predictive value of MRI plaque imaging, researchers performed carotid artery ultrasound and MRI on 946 asymptomatic patients from the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA).
The researchers used ultrasound to assess carotid wall thickness and MRI to define carotid plaque composition and the remodeling index, a measure of changes in vessel size. Imaging results were compared with cardiovascular events, including heart attacks, stroke and death, for an average of 5.5 years after examination.
“We studied asymptomatic individuals with a low risk of cardiovascular events at baseline and used noninvasive imaging to predict the risk of an event downstream,” said David A. Bluemke, M.D, Ph.D., from the National Institutes of Health Clinical Center in Bethesda, Md.
Cardiovascular events occurred in 59 of the patients. Abnormal thickening of the carotid artery wall and the presence of a lipid core and calcium in the internal carotid artery on MRI were significant predictors of subsequent events. A lipid core was present in almost half of the patients who had an event, compared with only 17.8 percent of those who did not have an event.
“The primary factors that predicted future risk were measures of vessel wall thickness in combination with the presence or absence of a lipid core,” Bluemke said. “The presence of a lipid core was 50 percent more common in people who had subsequent events.”
Use of MRI improved the reclassification of baseline cardiovascular risk in the study group. When both the carotid remodeling index and lipid core were used for risk stratification, approximately 16 percent more patients with events and 7 percent without events were correctly reclassified compared with the use of traditional risk factors.
“The results bolster the use of MRI as a surrogate marker of efficacy in therapeutic studies and point to a role in determining which patients might need more aggressive treatments,” Bluemke said. “As risk factor prediction gets better, we’ll be able to screen more intelligently and use more intensive treatments in those individuals who face a higher risk of cardiovascular events.”
Bluemke said sequences for plaque composition could be readily added to existing carotid MRI angiography protocols for clinical purposes.
“Carotid MRI has significant advantages,” he said. “The results are more reproducible than those of ultrasound.”
Availability and cost effectiveness could limit the use of MRI, Bluemke said. However, ultrasound and computed tomography (CT) are viable alternatives for screening, he said, especially with improvements in CT dose reduction.
For more information: radiology.org


 January 05, 2026
January 05, 2026 









