May 22, 2012 — New long-term data from the DIVERGE study presented at EuroPCR 2012 showed that the use of the Axxess drug-eluting stent (DES) for the treatment of complex coronary bifurcation lesions resulted in low levels of both MACE (major adverse cardiac events) and VLST (very late stent thrombosis) over a four-year period.
DIVERGE is a prospective, single-arm, multi-center study of 302 patients with de novo bifurcation lesions across 14 sites in Europe, Australia and New Zealand. It is the largest study conducted to date with a DES specifically designed for treating coronary bifurcation lesions. The Axxess DES is a self-expanding bifurcation stent that releases Biolimus A9 (BA9) from an abluminal biodegradable polymer coating. Following implantation of Axxess, the side branch treatments were left at the operators’ discretion. Additional conventional sirolimus-eluting stents (SES) were placed in 21.7 percent of the distal parent and/or side branch vessels. In 64.7 percent of the cases both branches were treated with an additional SES.
At four years post-procedure, 96.7 percent of patients originally enrolled in the study (292) were available for follow-up. The cumulative rate of MACE was 18.5 percent. The occurrences of the individual components were 5.1 percent for death, 7.9 percent for myocardial infarction and 10.6 percent for ischemia-driven target lesion revascularization (TLR).
There were only three cases of Academic Research Consortium (ARC)-defined definite VLST, all of which involved at least one SES; just one of these cases also involved Axxess. No VLST events were observed in Axxess patients between years three and four of the study.
"These long-term results from DIVERGE are important because of the frequent presentation of bifurcation lesions in our daily clinical practice," said principal investigator Stefan Verheye, Antwerp Cardiovascular Institute, Belgium. "These types of lesions are associated with higher complication and restenosis rates compared to conventional lesions. The four-year results confirm the earlier results already presented, and strengthen the evidence that the Axxess stent is a safe and effective alternative for patients with certain bifurcation lesions."
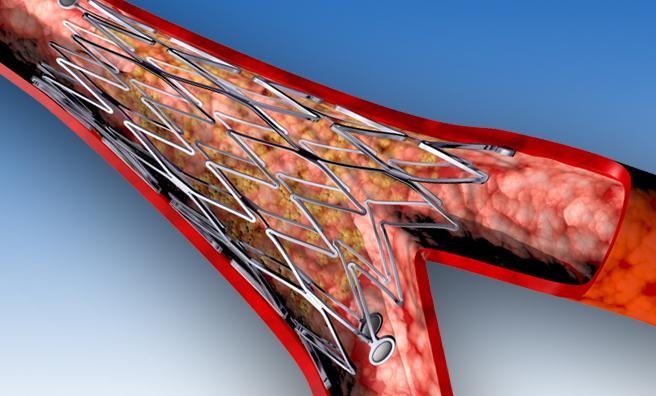
The Axxess bifurcation DES consists of a conical-shaped, self-expanding nitinol (nickel/titanium) stent platform, specifically designed to conform to the shape of the bifurcation anatomy. It has been tailored to reconstruct the bifurcation without creating a false carina (the ridge where the two vessels join), lowering the risk of uncovered struts at the flow divider. The stent is coated with a biodegradable polylactic acid polymer that releases BA9, an anti-restenotic drug designed by Biosensors specifically for use with DES. Both BA9 and the biodegradable polymer are vital components of the BioMatrix DES family.
Biosensors received CE mark approval for Axxess in April 2011, supported by the positive nine-month results from the DIVERGE trial, which were published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology in March 2009. Those results demonstrated low overall rates of MACE (7.6 percent), restenosis (0.7 percent) and late stent thrombosis (0.3 percent) in patients treated with Axxess. Axxess is now available in most major markets worldwide.
For more information: www.biosensors.com


 January 05, 2026
January 05, 2026 









