July 27, 2011 – Micell Technologies Inc. announced that it has completed patient enrollment in its DESSOLVE II CE mark clinical study of the MiStent drug-eluting coronary stent (DES) system. MiStent is an ultra-thin DES distinguished by a rapid-absorbing drug/polymer coating formulation. Enrollment of 183 patients across 26 study centers throughout Europe and New Zealand was accomplished ahead of schedule.
Micell previously announced that, based on results observed in the DESSOLVE I first-in-human trial, the sample size in the DESSOLVE II CE mark study was reduced from 270 to 171 subjects.
The DESSOLVE II trial is a multicenter study of patients with documented stable or unstable angina pectoris. The primary endpoint is superiority of the MiStent DES in minimizing in-stent late lumen loss at nine months as measured by the angiography core laboratory in de novo lesions ranging in diameter from 2.5 to 3.5 mm and amenable to treatment with a maximum 30 mm length stent.
"The coating on the MiStent DES differs substantially from those associated with commercially available DES technologies. The coating is engineered to clear the stent within 45 to 60 days and provide controlled and sustained delivery of sirolimus over a period of months, while limiting vascular exposure to the polymer coating to less than 90 days. As a result, we expect the MiStent DES could optimize sirolimus therapy by reducing the risk of complications such as late stent thrombosis, while suppressing neointimal hyperplasia and related healing responses to arterial injury that lead to restenosis," said Arthur J. Benvenuto, chairman and chief executive officer of Micell.
The MiStent DES is designed to optimize healing in patients with coronary artery disease. Micell's rapid-absorbing drug/polymer formulation is intended to precisely and consistently control drug elution and polymer exposure duration to reduce the safety risks associated with current commercially available drug-eluting stent technologies.
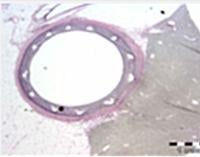
Using the antiproliferative drug sirolimus and PLGA polymer, Micell's patented supercritical fluid technology allows a rigorously controlled drug/polymer coating to be applied to a bare-metal stent. The MiStent DES leverages the benefits of Eurocor's (CE marked) Genius Magic cobalt chromium coronary stent system, which has demonstrated excellent deliverability, conformability and flexibility. Good laboratory practices (GLP) pre-clinical trials have shown that the drug/polymer coating is eliminated from the MiStent DES within 45 to 60 days. In addition, the polymer-based coating is fully absorbed in tissue by 90 days in vivo, at which point the bare-metal stent remains. The MiStent DES is currently being evaluated in international clinical studies.
The MiStent DES is an investigational device. It is not yet approved or available for sale in any market.
For more information: www.micell.com


 January 05, 2026
January 05, 2026 









