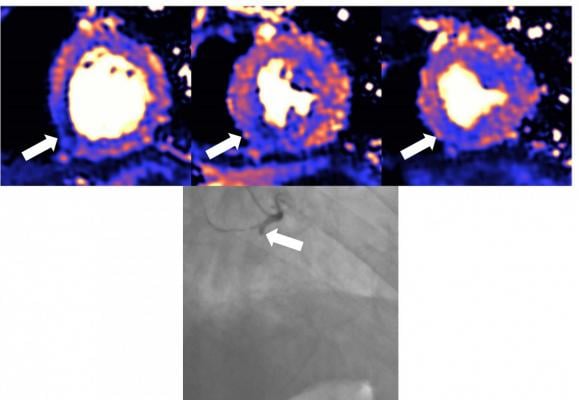
MRI scan of a damaged heart. Blue means reduced blood flow, orange is good blood flow. In this figure the inferior part of the heart shows dark blue, so the myocardial blood flow is very reduced. The angiogram shows the coronary artery which supplies the blood to this part of the heart is occluded. The three colored MRI images show different slices of the heart — the basal mid and apical slices. Image courtesy of European Heart Journal
March 17, 2021 — Around 50% of patients who have been hospitalized with severe COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) and have damage to their hearts with elevated troponin levels and ischemia and coronary blocks shown on imaging. The injury was detected by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans at least a month after discharge, according to new findings published in February in the European Heart Journal.[1]
Damage includes inflammation of the heart muscle (myocarditis), infarction, ischemia, or a combinations of all three.
The study of 148 patients from six acute hospitals in London is the largest study to date to investigate convalescing COVID-19 patients who had raised troponin levels indicating a possible problem with the heart.
Troponin is released into the blood when the heart muscle is injured. Raised levels can occur when an artery becomes blocked or there is inflammation of the heart. Many patients who are hospitalized with COVID-19 have raised troponin levels during the critical illness phase, when the body mounts an exaggerated immune response to the infection. Troponin levels were elevated in all the patients in this study who were then followed up with cardiac MRI scans after discharge in order to understand the causes and extent of the damage.
"Raised troponin levels are associated with worse outcomes in COVID-19 patients," explained Professor Marianna Fontana, professor of cardiology at University College London (U.K.), who led the research together with Dr. Graham Cole, a consultant cardiologist at Imperial College London. Patients with severe COVID-19 disease often have pre-existing heart-related health problems including diabetes, raised blood pressure and obesity. During severe COVID-19 infection, however, the heart may also be directly affected. Unpicking how the heart can become damaged is difficult, but MRI scans of the heart can identify different patterns of injury, which may enable us to make more accurate diagnoses and to target treatments more effectively."
The researchers investigated COVID-19 patients discharged up until June 2020 from six hospitals across three NHS London trusts: Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust, Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust and University College London Hospital NHS Foundation Trust. Patients who had abnormal troponin levels were offered an MRI scan of the heart after discharge and were compared with those from a control group of patients who did not have COVID-19, as well as from 40 healthy volunteers.
"The recovering COVID-19 patients had been very ill; all required hospitalization and all had troponin elevation, with around one in three having been on a ventilator in the intensive care unit," said Prof. Fontana.
"We found evidence of high rates of heart muscle injury that could be seen on the scans a month or two after discharge. Whilst some of this may have been pre-existing, MRI scanning shows that some were new, and likely caused by COVID-19. Importantly, the pattern of damage to the heart was variable, suggesting that the heart is at risk of different types of injury. While we detected only a small amount of ongoing injury, we saw injury to the heart that was present even when the heart's pumping function was not impaired and might not have been picked up by other techniques. In the most severe cases, there are concerns that this injury may increase the risks of heart failure in the future, but more work is needed to investigate this further."
The function of the heart's left ventricle, the chamber that is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood to all parts of the body, was normal in 89% of the 148 patients but scarring or injury to the heart muscle was present in 80 patients (54%). The pattern of tissue scarring or injury originated from inflammation in 39 patients (26%), ischemic heart disease, which includes infarction or ischemia, in 32 patients (22%), or both in nine patients (6%). Twelve patients (8%) appeared to have ongoing heart inflammation.
"Injury relating to inflammation and scarring of the heart is common in COVID-19 patients with troponin elevation discharged from hospital, but is of limited extent and has little consequence for the heart's function," Fontana said.
"These findings give us two opportunities," she continued. "Firstly, to find ways of preventing the injury in the first place, and from some of the patterns we have seen, blood clotting may be playing a role, for which we have potential treatments. Secondly, detecting the consequences of injury during convalescence may identify subjects who would benefit from specific supporting drug treatments to protect heart function over time."
The findings of the study are limited by the nature of patient selection and included only those who survived a coronavirus infection that required hospital admission.
"The convalescent patients in this study had severe COVID-19 disease and our results say nothing about what happens to people who are not hospitalized with COVID, or those who are hospitalized but without elevated troponin. The findings indicate potential ways to identify patients at higher or lower risk and suggest potential strategies that may improve outcomes. More work is needed, and MRI scans of the heart have shown how useful it is in investigating patients with troponin elevation," Fontana said.
The study is also the subject of a discussion between Prof. Fontana and Prof. Eike Nagel, at the Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (SCMR) annual meeting on in February, where it was presented for the first time.[2] Prof. Nagel, director of the Centre for Cardiovascular Imaging at Deutsches Zentrum Für Herz-Kreislauf-Forschung (DZHK), Frankfurt, Germany, is the senior author on an earlier paper that found ongoing heart problems in up to 78% of COVID-19 patients who were less sick and most of whom did not require admission to hospital.[3]
Related COVID Cardiology Content:
The Long-term Cardiovascular Impact of COVID-19
VIDEO: Antithrombotic Prophylaxis in COVID-19 Patients — Interview with Behnood Bikdeli M.D.
COVID-19 Changes Properties Blood Cells
Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) and the Heart—Is Heart Failure the Next Chapter?
PHOTO GALLERY: How COVID-19 Appears on Medical Imaging
COVID-19 Blood Vessel Damage May Cause Brain Fog and Other Long-hauler Symptoms
Overview of Randomized Trials of Antithrombotic Therapy for COVID-19 Patients
COVID-19 Can Kill Heart Cells and Interfere With Contraction
References:
1. Tushar Kotecha et al. Patterns of myocardial injury in recovered troponin-positive COVID-19 patients assessed by cardiovascular magnetic resonance. European Heart Journal. Published 18 February 2021. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehab075.

 January 28, 2026
January 28, 2026