September 20, 2017 — Catheter ablation to treat an irregular heartbeat, which limits or eliminates patients’ exposure to radiation, should be more widely adopted by physicians, according to a new review article. The article was written by NewYork-Presbyterian and Weill Cornell Medicine cardiologists and published in the June print issue of Heart Rhythm and previously published online. In it, they posit that the primary obstacle to the procedure’s widespread use – physicians’ discomfort with a different visual tool – can be overcome with training and experience.
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a condition that affects as many as 6.1 million Americans and is characterized by an irregular, often rapid heart rate caused by a misfiring of electrical impulses. Physicians commonly treat the condition using a minimally invasive procedure called catheter ablation, in which doctors insert thin, flexible wires into veins, snaking them up into the heart. Once there, physicians apply radiofrequency energy or freezing temperatures to eliminate the abnormal electrical pathways, restoring the heart’s regular rhythm.
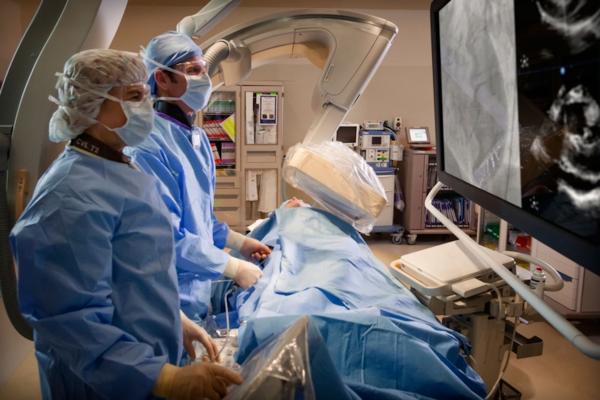
To guide this procedure, many cardiologists rely on fluoroscopy, which uses a continuous X-ray beam to visualize the heart. While effective, the technique exposes both the care team and patient to high doses of radiation.
“The amount of fluoroscopy received by a patient during a routine AF ablation procedure is estimated to be the equivalent of the dose of radiation a patient would receive with 830 X-rays,” said lead author Bruce Lerman, M.D., chief of the Division of Cardiology and director of the Cardiac Electrophysiology Laboratory at NewYork-Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Center and Weill Cornell Medicine, where he is also the H. Altschul Master Professor of Medicine. “In our hands, the vast majority of AF patients do not require fluoroscopy, resulting in no radiation exposure to the patient or the electrophysiologist performing the procedure.”
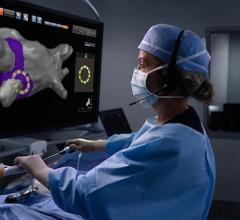
To accomplish fluoroless catheter ablation, the NewYork-Presbyterian and Weill Cornell Medicine team use technology that emits high-frequency sound waves, known as intracardiac echocardiography (ICE), to create a complete and precise image of the heart. In addition, the use of computerized three-dimensional mapping systems and pre-procedural cardiac imaging can further guide the procedure. Weill Cornell Medicine electrophysiologists believe that physicians around the country can embrace fluoroless ablation of atrial fibrillation by challenging entrenched practices.
“Although the concept of fluoroless catheter ablation was introduced several years ago, it has yet to gain wide adoption, mostly because many electrophysiologists were trained to rely on X-ray imaging and are reluctant to trust ICE,” said co-author Jim Cheung, M.D., director of clinical electrophysiology research and cardiac electrophysiology fellowship training at NewYork-Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Center and associate professor of medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine. Cheung is a consultant for and has received fellowship grant support from Biosense Webster, a manufacturer of electrophysiology devices. “This concern can be remedied with experience. For some, the learning curve can be steep, but generally, the skill set can be readily acquired. By thoughtfully modifying the way the procedure is performed, we can significantly reduce the radiation risk in the process,” he said.
“We are currently training our fellows to utilize this technique in an effort to guide the next generation of cardiologists to become well-versed in fluoroless ablation,” Cheung said.
“The most critical requisite for performing fluoroless catheter ablation of AF is a willingness to relinquish an old habit,” said Lerman, who is also a consultant for Biosense Webster. “Doing so will have a tremendous advantage for both patients and healthcare professionals.”
Read the related article "What is New in Electrophysiology Technologies."
For more information: www.heartrhythmjournal.com


 February 06, 2026
February 06, 2026