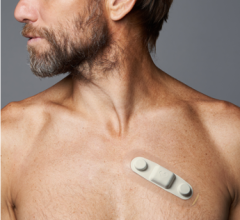
March 12, 2014 — iRhythm Technologies Inc., a healthcare information services company, announced that new study data support the use of its ZIO Service to help identify underlying cardiac arrhythmias in patients who have had a stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA). The ZIO Service enables long-term continuous monitoring — using a noninvasive, small, wearable patch — to detect sporadic heart rhythm disturbances, including atrial fibrillation (AF), which is associated with an increased risk of stroke. The new findings were presented in an abstract Wednesday at the International Stroke Conference 2014 in San Diego, Calif.
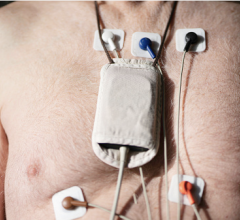
“Physicians need to know if stroke or TIA patients have an underlying cardiac arrhythmia, which may have caused their neurological event, as this will impact treatment to help prevent a recurrence,” said Maarten Lansberg, M.D., Ph.D., study author and assistant professor of neurology and neurology sciences at the Stanford University Medical Center. “Current cardiac monitoring options are limited in their ability to capture arrhythmias, and can be difficult for patients to use or tolerate. Our findings showed that the ZIO Patch was worn by stroke and TIA patients for long periods of time, and that it identified a significant number of arrhythmia events that would have been missed by traditional Holter monitors, due to their shorter wear times.”
For the study, Stanford researchers analyzed data for 1,171 patients who wore the ZIO Patch to detect potential heart arrhythmias following a stroke or TIA. They found that patients wore the monitor for an average of 10.9 days, which is significantly longer than the 24-48 hours for which the traditional Holter monitor is typically worn. Symptomatic and asymptomatic AF was found in 4.8% of all reports and supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) — a broader category of atrial arrhythmias excluding AF — was present in 51% of records. Further, in one out of seven patients (14.3%), the first case of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (PAF) occurred more than 48 hours after the start of monitoring, meaning it would have been missed by the Holter monitor.
For more information: www.irhythmtech.com


 March 31, 2025
March 31, 2025