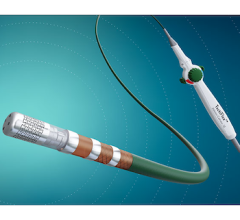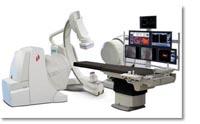
August 5, 2009 – Stereotaxis Inc. said today clinicians performed more than 2,500 procedures with the magnetic irrigated catheter since its commercial release, and the major adverse cardiac event (MACE) rate for magnetic procedures remains at 0.1 percent.
"The irrigated tip is a great asset for creating deep lesions in patients with ventricular tachycardias in the setting of structural heart disease," said Raul Weiss, M.D., associate professor of medicine at Ohio State University and an electrophysiologist at the Ross Heart Hospital in Columbus. "The Thermocool magnetic catheter creates deeper lesions because the catheter remains in contact with the beating heart. The irrigation allows me to deliver more energy, creating a larger lesion. You don't have to push on the catheter like you do with a manual catheter, so the likelihood of perforation, I think, is significantly reduced."
Overall, the Niobe Remote Magnetic Navigation System has been utilized in nearly 23,000 cases worldwide. These include ablations of a wide variety of cardiac arrhythmias in all four chambers of the heart and across a broad spectrum of patients ranging from pediatric to geriatric. Included in the Niobe clinical experience are several very compelling procedures in patients with congenital heart defects and patients with peripheral vascular occlusive disease. Altogether this represents the broadest range of cardiovascular applications achieved with any commercial remote magnetic, robotic or mechanical navigation system presently in the marketplace.
Stereotaxis designs, manufactures and markets an advanced cardiology instrument control system for use in a hospital's interventional surgical suite to enhance the treatment of coronary artery disease and arrhythmias. The Stereotaxis System is designed to enable physicians to complete more complex interventional procedures by providing image guided delivery of catheters and guide wires through the blood vessels and chambers of the heart to treatment sites. This is achieved using computer-controlled, externally applied magnetic fields that govern the motion of the working tip of the catheter or guide wire, resulting in improved navigation, shorter procedure time and reduced X-ray exposure.
For more information: www.stereotaxis.com


 February 06, 2026
February 06, 2026