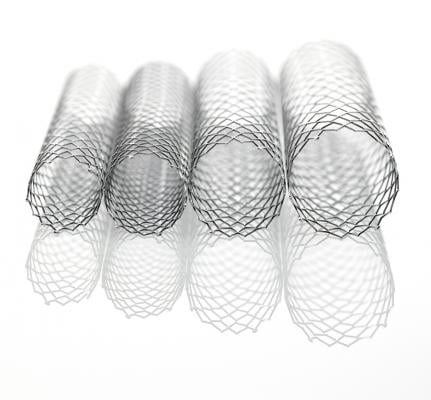
July 16, 2015 — Medtronic plc announced that its Protege GPS self-expanding peripheral stent system has received approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of stenotic lesions of the common and external iliac arteries.
The news follows the nine-month results of the DURABILITY Iliac study, which were presented at the 2014 VIVA (Vascular Interventional Advances) conference in Las Vegas. The results demonstrated the safety and effectiveness of the Protege GPS peripheral stent system in the treatment of stenotic lesions of the common and external iliac arteries. The prospective, multi-center, non-randomized clinical study demonstrated 95.8 percent nine-month primary patency (the ability for the treated artery to remain open) by Kaplan-Meier analysis and 98.6 percent freedom from target vessel revascularization (no repeat procedure).
"When used for iliac angioplasty and stenting, the Protege GPS self-expanding peripheral stent system demonstrated excellent patency rates even in difficult-to-treat calcified lesions," said Peter Faries, M.D., co-national principal investigator of the DURABILITY Iliac study, Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New York. "Data from the DURABILITY Iliac study confirms the safety and effectiveness of the Protege GPS stent. It is gratifying to see that the FDA has approved this stent for the iliac indication."
Iliac stenosis occurs when plaque builds up in the iliac artery, which can block the blood supply to the entire leg. As a result, patients with iliac artery stenosis can experience pain that can limit mobility.
The self-expanding peripheral stent system allows physicians to treat iliac artery lesions and restore blood flow with large diameter stents through a low-profile 6 French delivery system. The stent is cut from a nitinol tube into an open lattice design and has tantalum radiopaque markers at the proximal and distal ends of the stent. Upon deployment, the stent achieves its predetermined diameter and exerts a constant, outward force to restore patency.
For more information: www.medtronic.com

 November 14, 2025
November 14, 2025