Getty Images
Coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) is cheaper, easier to use and its results are easier to understand than Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS), making it ideal for clinical trials of cardiovascular (and other) drug candidates. Additionally, advances in computing and artificial intelligence (AI) are enabling precise measurement of changes in atherosclerosis disease progression, including the ability to identify, classify and quantify plaque tissue structure and composition. Importantly, plaque progression has been established as a surrogate endpoint for increased cardiovascular (CV) events and risk, another reason CCTA is excellent for evaluating CV therapeutics in clinical trial settings.
Coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) of the heart and coronary vessels using contrast fluid and stress to determine whether they have been narrowed.
IVUS and CCTA: Substance Over Surface
IVUS uses a catheter with a distal miniaturized ultrasound transducer that is threaded through the vasculature into the coronary vessels. The sound waves reflected from the interior vessel walls are processed to produce images of the endothelial lumen. IVUS images can provide information about the amount and type of plaque buildup, one measure of risk for heart attack.
However, as an invasive procedure, IVUS does pose some risk to the patient, including the potential for complications including dissection, perforation, arrhythmia, thrombosis and vasospasm. IVUS scans are more expensive and time-consuming than CCTA scans, and, crucially, although they generate images of the surface of the interior vessel wall, they don’t assess the extent or composition of plaque deposits.
Like IVUS, CCTA is used to evaluate plaque buildup in the coronary arteries; unlike IVUS, it is non-invasive, removing the risks of IVUS detailed above. Instead, the patient is injected with a contrast agent containing iodine; high-speed CT scans provide detailed images of a variety of tissue types, including coronary plaque. CCTA requires less space and fewer healthcare providers to administer, and because it requires less time per procedure, improves workflows and efficiency. Although non-invasive, CCTA does pose a slight risk due to radiation exposure. It also carries a small risk of reaction to the contrast agent.
The Value of Plaque Progression in Pharma Trials
In pharmaceutical trials, CCTA is useful in studying a variety of drugs aimed at treating cardiovascular disease, including diabetes agents, anti-cholesterol drugs (either LDL-lowering or HDL-raising), triglycerides and statins, because it enables the tracking of plaque progression – a reliable endpoint in CV drug studies. In fact, several ongoing Phase IIB trials are designed to be go/no go largely based on CCTA results, and every major pharma player in cardiology is conducting drug trials using the technology.
That’s in part because the progression or regression of plaque is increasingly regarded as a more significant outcome than major adverse cardiac events (MACE).
Consider the JUPITER trial, a nearly 18,000-patient study of rosuvastatin (Crestor). Patients with low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels of less than 130 mg per deciliter, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels of 2.0 mg per liter or higher, were randomized to receive either 20 mg of rosuvastatin or placebo daily.
Although JUPITER showed a roughly 40% reduction in MACE, those results received less attention than data showing that treatment with rosuvastatin slowed the development of coronary plaque, which was a large focus in lectures and meeting presentations following study completion.
In addition, physicians understand and have confidence in CCTA results in a way they don’t for IVUS, which can help with marketing efforts, because it makes it much easier for sales staff to demonstrate a drug’s effects.
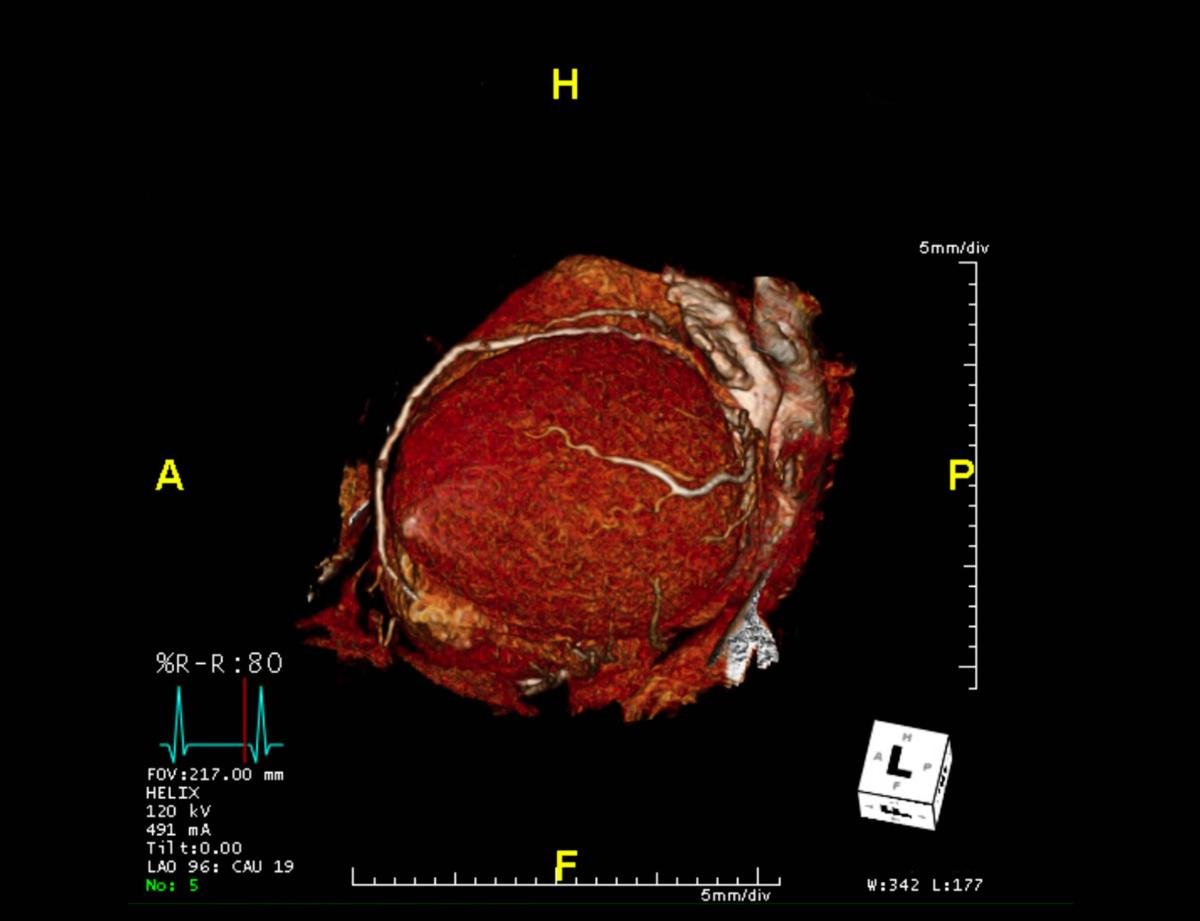
CTA Coronary artery 3-D rendering image from the screen.
Adding Power to CCTA with AI
Add-ons powered by AI and machine learning make CCTA exponentially more powerful, by providing additional metrics that improve the ability to evaluate a drug’s effects. One such technology is FDA-approved for quantifying atherosclerotic plaque characteristics compared to histopathology, enabling trial researchers to track the progression or regression of multiple plaque types, including lipid rich necrotic core (LRNC) plaque in the experimental cohorts of their trials.
One example of this is the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled EVAPORATE trial, which was designed to use CCTA to assess the efficacy of icosapent ethyl (Vascepta) in reducing plaque burden among patients with known angiographic coronary artery disease (CAD), who were also on statins.
In EVAPORATE, 80 patients were divided into two cohorts; the control arm received a placebo, and the experimental arm took 4 g of the drug daily. EVAPORATE showed that the drug reduces low attenuation plaque volume at 18 months, compared with placebo, as assessed by CCTA. The primary outcome, change in low attenuation plaque volume, was -0.3 vs. 0.9 mm3 (p = 0.006). Secondary outcomes included change in total plaque volume: -9% vs. 11% (p = 0.002); change in total noncalcified plaque: -19% vs. 9% (p = 0.0005); change in fibrofatty plaque: -34% vs. 32% (p = 0.0002); and change in triglycerides: -89.3 vs. -92.1 mg/dl (p = 0.91). There was also a reduction in total plaque volume, as well as other plaque parameters.
In an additional analysis, data from EVAPORATE were reviewed using AI-powered software to measure changes in plaque morphology characteristics, including LRNC, fibrous cap thickness and intraplaque hemorrhage (IPH). The study evaluated the change in plaque characteristics using CCTA at nine and 18 months, using histologically defined terms for endpoints which could only be assessed using the AI-powered software — a great improvement over subjective radiological appearance that gives us a window onto the mechanism of the disease process.
That software is also being used in at least seven ongoing trials, both retrospective and prospective, examining plaque characterization, prediction of MACE, prospective care determination, plaque morphology prediction of composite periprocedural complications, and plaque morphology to predict stroke.
Benefits Beyond the Research Setting
CCTA is a better tool than IVUS in helping pharmaceutical companies investigate cardiovascular drug candidates, but its promise extends beyond the research arena.
Recent innovations are enabling a new era of arterial plaque evaluation. Machine learning and AI technologies are opening new avenues of investigation into soft and vulnerable plaques. The resultant improved risk assessment, and the ability to track preventive treatments, is enabling a shift from reactive treatment of coronary episodes to active prevention of disease progression — before atherosclerosis progresses to angina, acute coronary syndrome or heart attack.
View the Cardiac CT Systems Comparison Chart here

Matthew Jay Budoff, MD, FACC, FAHA, is a professor of medicine at UCLA’s David Geffen School of Medicine, and the Endowed Chair of Preventive Cardiology at the Lundquist Institute at Harbor-UCLA Medical Center.

 January 28, 2026
January 28, 2026