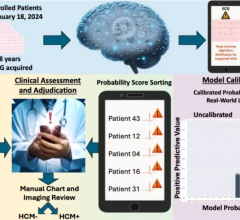
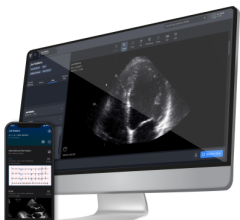
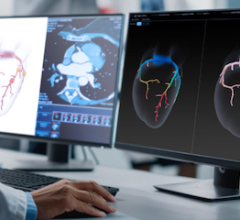
Basic artificial intelligence is already incorporated into several premium echocardiography systems. This example is from the Philips Epiq, where the AI takes 3-D datasets and automatically identifies and segments the cardiac anatomy. It then extracts the best images for each of the standard echocardiogram views to eliminate variation between operators. The next generation echo AI software will pull in data from the electronic medical records and imaging data to offer suggested diagnoses.
Artificial Intelligence has a multitude of impacts on our daily lives, from recommending movies based upon your Netflix viewing habits, to assisting pilots with flying modern jets. One of the most significant applications, however, will be in healthcare.
In 2019, we have already seen success stories of how artificial intelligence (AI) is being used to treat patients. For instance, IDx-DR is the first ever autonomous AI system cleared by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to provide diagnostic support. It works by detecting signs of diabetic retinopathy in ocular images, then applies an algorithm to produce a binary diagnosis in a matter of minutes.
Another way that AI can assist clinicians is by providing earlier diagnosis of conditions that could lead to early patient mortality. This is especially useful when it comes to diagnosing cardiovascular diseases, which kill around 17.9 million people every year – adding up to roughly 31 percent of all global deaths.
So how might AI change the game for clinicians and patients alike?
AI’s Potential in Cardiovascular Diagnosis
Analyzing echocardiograms can be difficult, with up to 20 percent of patients currently misdiagnosed. This is partly because it’s difficult to spot the signs of coronary artery disease (CAD) with the naked eye. However, we can use AI alongside traditional diagnosis techniques to improve upon these results.
For example, the FDA-pending Ultromics’ EchoGo software uses artificial intelligence to extract a multitude of data points from an echocardiographic . These are data points that can not be seen by the naked eye. Clinicians can then use this data to make more informed decisions.
How Do We Train AI for Cardiovascular Diagnosis?
What allows a computer to recognize the signs of CAD, and how reliably does it provide such diagnostic support? The answer lies in a combination of clever programming and a very large dataset.
Training an AI algorithm of this nature uses a form of “supervised machine learning,” which means it uses thousands of images collected from people who are known to have disease because they either went on to have a heart attack or had more invasive tests to prove they had a problem. The machine can be shown supervised examples of scans typical for patients with the disease and, also, examples of people who were eventually found to be free of disease. The machine uses all the information in the image to learn the patterns in the images that best pick out the patients with heart problems.
Once the key pattern has been identified, the machine can then start looking for it in images collected from new patients. This can be used to provide a diagnostic support recommendation that predicts how likely that patient is to have a heart attack in the next year and potentially avoid the need for further invasive tests.
Will AI Replace Clinicians?
One common fear regarding AI in the workplace is that machines could replace humans, however, this scenario is extremely unlikely. Diagnosis is merely one stage of the treatment process, and clinical expertise and human intervention will continue to be invaluable throughout the diagnostic and treatment pathway. But AI can be a powerful tool for clinicians, helping them potentially make a more accurate diagnosis.
Human beings have broader general intelligence than AI, which tends to have much narrower, more task specific focus in its current state. We can be more flexible than a computer in how we approach problems, and human beings are capable of showing empathy towards patients. In this respect, the human touch is irreplaceable. What AI can do is make diagnosis quicker and more reliable, allowing the clinicians to focus more of their energy on the “care” part of healthcare.
Will AI be Able to Diagnose CAD With 100 Percent Accuracy?
AI-driven diagnostics can improve as its training dataset or model programming improves, so there is continued potential for diagnostic accuracy to increase. However, it is unlikely that we will reach a 100 percent accuracy level.
This is because diagnosis can depend on a range of issues that the AI has not been trained to consider, such as unexpected changes in patterns of disease or previously unknown factors in a patient history. It is possible, in theory, to address these factors by using larger and larger datasets and combining other types of clinical and non-clinical data.
However, there is a risk that AI can learn incorrectly if it is just presented with lots of data that has not been collected carefully and checked to be accurate. Being shown the wrong advert by AI software does not matter too much. Being given the wrong diagnosis does. Therefore, although AI offers exceptional accuracy in many focused tasks, for the foreseeable future, it will do this by supplementing the existing judgement and training of clinical experts.
The Future of AI in Cardiology
Ultimately, nobody in the field of cardiology should fear AI, nor should patients worry about having a computer working alongside a trained human clinician.
By improving the diagnosis of conditions like CAD, artificial intelligence could have a hugely positive impact on care delivery. It will provide a tool to assist clinicians, helping them to make a more accurate diagnosis. By doing so, we can help reduce the number of patients being sent for unnecessary surgical procedures or sent home with a potentially fatal disease.
On this basis, many clinicians have already realized that the sensible approach is to embrace AI-driven diagnosis and are already adopting and using AI the methods in their routine care. AI-driven diagnostics for CAD are now also becoming a reality.
Is AI the future of cardiology? It will certainly be part of it, and if we can use it to improve diagnostic results it could help us save millions of lives and billions of dollars globally.
Editor’s note: Ross Upton is CEO and academic co-founder of Ultromics. He is specialized in utilizing computational technologies to build diagnostic algorithms for cardiac imaging. He has a background in medical sciences received multiple grants for technology innovation.
Related AI in Cardiology Content:
Applications for Artificial Intelligence in Cardiovascular Imaging
VIDEO: Artificial Intelligence Applications for Cardiology — Interview with Anthony Chang, M.D.
How Machine Learning Empowers Echo Users Today
PODCAST: How Technology Is Changing Cardiology With Partho P. Sengupta, M.D.
FDA Proposes New Review Framework for AI-based Medical Devices
VIDEO: How Hospitals Should Prepare for Artificial Intelligence Implementation — Interview with Paul Chang, M.D.
PODCAST: Fitting Artificial Intelligence Into Cardiology With Anthony Chang, M.D.
DiA Imaging Analysis Introduces LVivo SAX Ultrasound Analysis Tool
Ebit and DiA Imaging Analysis Partner on AI-based Cardiac Ultrasound Analysis
Bay Labs Announces New Data on EchoGPS, AutoEF AI Software at ACC.19
How AI Can Unlock Data in CT and MRI Scans


 September 24, 2025
September 24, 2025