October 12, 2022 — Cleveland Clinic researchers have identified a common diabetes medication, metformin, as a possible treatment for atrial fibrillation.
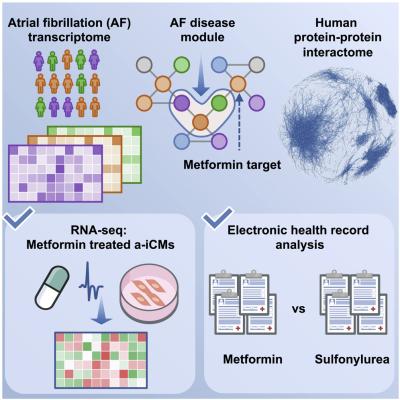
The study, published in Cell Reports Medicine, built on ongoing collaborative Cleveland Clinic research to support further investigation into metformin as a drug repurposing candidate. Researchers used advanced computation and genetic sequencing to determine that metformin’s targets overlap significantly with genes dysregulated in atrial fibrillation.
“Finding drugs or procedures to treat atrial fibrillation is difficult because of potential serious side effects," said Mina Chung, M.D., senior author of the study who is in Cleveland Clinic’s Department of Cardiovascular Medicine in the Heart, Vascular and Thoracic Institute. "There is a significant need for new treatments for atrial fibrillation as there have been no new drugs approved in more than a decade.”
“It's not that we've found a new drug target where it takes 20 years to test this in individuals,” said Jessica Castrillon Lal, the study’s first author and a fifth-year graduate student in the Cleveland Clinic Molecular Medicine program.
“We can cut off 10+ years in the drug development pipeline. We already have the information there. We just have to test it in a very computationally efficient way, such as artificial intelligence technology,” said Feixiong Cheng, Ph.D., co-senior author of the study who is Associate Staff at the Genomic Medicine Institute in Cleveland Clinic’s Lerner Research Institute.
The analysis found metformin targeted 30 genes associated with atrial fibrillation, with direct effects on gene expression for eight. Eight other candidate drugs surfaced in the analysis, but researchers were able to identify metformin as the most promising candidate through testing and reviewing outcomes in large stores of patient data.
Castrillon Lal conducts research in Dr. Cheng’s lab, which uses network medicine approaches to find candidate drugs for repurposing, creating vast networks of molecular interactions. For this study, researchers winnowed down a list of 2,800 FDA-approved treatments by analyzing three data sources: a map of interactions between proteins called an “interactome”; a network of genes associated with atrial fibrillation; and each medicine’s molecular or genetic targets.
Atrial fibrillation is the most common type of heart arrhythmia in the world and can lead to complications, including stroke and heart failure. Treatments have been primarily directed toward trying to prevent the arrhythmia using drugs targeting the electrical system, including ion channels in the heart, or using catheter ablation to isolate the pulmonary veins where initiating beats of atrial fibrillation occur.
However, side effects, limited success and potential complications can limit these approaches.
The research was conducted in collaboration with labs led by Dr. Chung, Dr. Cheng, David Van Wagoner, Ph.D.; Jonathan Smith, Ph.D., Department of Cardiovascular and Metabolic Sciences; and John Barnard, Ph.D., Department of Quantitative Health Sciences in the Lerner Research Institute.
Prior work from Drs. Chung, Smith, Van Wagoner, and Barnard had also identified the enzyme AMPK as a potential key regulator for metabolic stress. Metabolic stress has been associated with atrial fibrillation.
This work is related to a recently awarded $14.2 million grant from NIH to investigate new atrial fibrillation treatments using genomic data. Researchers further supported results of the network analyses with experiments on live beating heart cells grown from human stem cells, showing favorable effects of metformin on gene expression.
For more information: www.clevelandclinic.org


 January 05, 2026
January 05, 2026 









