June 15, 2017 — In patients undergoing transradial primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) for ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), there was no significant difference in the rate of a composite of death, myocardial infarction and stroke whether they were anticoagulated with bivalirudin or unfractioned heparin, according to a study published in May in Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC): Cardiovascular Interventions.
Using data from the National Cardiovascular Data Registry CathPCI Registry, researchers examined the records of 67,368 patients from 1,584 sites between 2009 to 2015 with STEMI who underwent primary PCI via radial access. Of these patients, 29,660 received bivalirudin and 37,708 received heparin. The groups did not differ substantially in mean age (60.3 and 60.4, respectively) or percentage of men (74.9 and 75 percent, respectively).
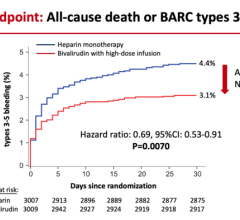
The researchers adjusted for multiple variables, including a propensity score reflecting the probability of receiving bivalirudin to account for patient differences between groups. After these adjustments, the odds ratio of the composite endpoint of death, myocardial infarction or stroke for bivalirudin versus heparin was not statistically significant (0.95); the odds ratio for acute stent thrombosis was 2.11 for bivalirudin versus heparin. Major bleeding rates were not significantly different.
Ion S. Jovin, M.D., FACC, the study’s lead author and medical director of the cardiac catheterization laboratories at McGuire Veterans Affairs Medical Center and associate professor of medicine at Virginia Commonwealth University, said that the study’s results are consistent with data from contemporary studies of patients with acute coronary syndrome and STEMI.
“Our sensitivity analysis provides some insights into direct comparisons of bivalirudin and heparin when GPIIb/IIIa inhibitors are forced out of the equation and suggests that in the direct comparison bivalirudin may have superior outcomes,” Jovin said. “However, our study showed that in the real world over a third of the patients with STEMI undergoing transradial PCI who receive heparin and about a fifth of patients who receive bivalirudin also receive GPIIb/IIIa inhibitors.”
The authors suggested that a randomized trial in patients treated exclusively via transradial primary PCI and anticoagulated with bivalirudin versus heparin as well as a cost-effectiveness analysis comparing heparin versus bivalirudin would help practitioners and hospitals make better decisions regarding anticoagulation in these patients.
For more information: JACC.org

 August 28, 2023
August 28, 2023