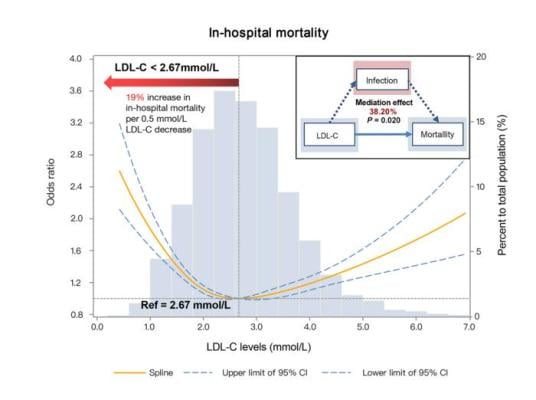
The U-shaped association between LDL-C level and all-cause mortality during hospitalization, and the mediation effect of infection in patients with acute ischemic stroke in the CSCA program. 804,855 patients were included. Abbreviations: LDL-C: low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; CSCA: Chinese Stroke Center Alliance. Image courtesy of Science China Press
June 28, 2023 — The general perception supports the mantra of “lower is better” for low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels in cardiovascular disease. However, during the acute stage of ischemic stroke, it is unclear how to interpret different LDL-C levels accurately. The evidence on clinical implication of LDL-C levels was mainly derived from long-term follow-up studies. The pathophysiological features of patients under the acute stage of ischemic stroke are different from the chronic stage. Concerns exist over whether low LDL-C levels may lead to adverse outcomes, such as increased mortality risk due to infection. The crosstalk between LDL-C and infection is also garnering increasing amounts of interest.
This study aimed to evaluate the association between LDL-C levels, post-stroke infection and all-cause mortality. 804,855 ischemic stroke patients were enrolled. Associations between LDL-C levels, infection, and mortality risk were estimated by multivariate logistic regression models. Mediation analysis was performed under counterfactual framework to elucidate the mediation effect of post-stroke infection.
The study found a U-shaped association between LDL-C and mortality risk in acute ischemic stroke patients. The lowest mortality risk was at an LDL-C level of 2.67 mmol/L. The association between LDL-C and all-cause mortality was 38.20% mediated by infection. Sensitivity analysis showed that after excluding patients with increasing numbers of cardiovascular risk factors, the U-shaped association remained consistent but the LDL-C interval with the lowest mortality risk increased progressively, where infection maintained prominent mediation effects. Subgroup analysis showed a consistent U-shaped association between LDL-C levels and mortality risk. The mediation effects of infection were largely consistent in subgroups of age ≥65 years, female, body mass index <25 kg/m2, and National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale ≥16.
Despite the known adverse effects of high LDL-C levels, in ischemic stroke patients, this study revealed that low LDL-C levels also indicate an increased risk of all-cause mortality during hospitalization, where post-stroke infection is an important mediating mechanism, indicating a potential causal chain of low LDL-C-infection-mortality in the acute stage of ischemic stroke. Further research is warranted to explore the risk-benefit relationship of approaches for rapid and substantial LDL-C reduction during the acute stage of ischemic stroke.
For more information: https://www.scichina.com/


 January 05, 2026
January 05, 2026 









