February 22, 2016 — A new study found that survival rates from cardiac arrest decrease the higher up in a high-rise building a person lives.
"Cardiac arrests that occur in high-rise buildings pose unique barriers for 911-initiated first responders," said Ian Drennan, lead author of the study published in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
"Building access issues, elevator delays and extended distance from the emergency vehicle to the patient can all contribute to longer times for 911-initiated first responders to reach the patient and start time-sensitive, potentially life-saving resuscitation," he said.
Drennan is a paramedic with York Region Paramedic Services and a researcher with Rescu, a group based at St. Michael's Hospital that studies emergency healthcare that begins outside of a hospital.
Looking at data from 8,216 adults who suffered an out-of-hospital cardiac arrest treated by 911-initiated first responders in the city of Toronto and nearby Peel Region from January 2007 to December 2012, they found 3.8 percent survived until they could be discharged from a hospital. Survival was 4.2 per cent for people living below the third floor and 2.6 percent for people living on or above the third floor.
But Drennan said when they went back and looked at the exact floor the patients lived on, they found decreased survival rates as the floors got higher. Survival above the 16th floor was 0.9 percent (of 216 cases, only two survived). There were no survivors to hospital discharge of the 30 cardiac arrests above the 25th floor.
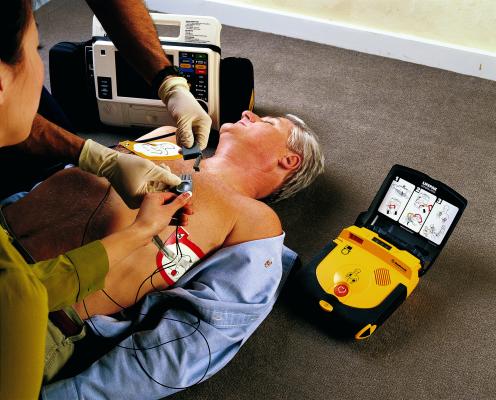
"Patients who survived tended to be younger, their cardiac arrest was more often witnessed by bystanders, and bystanders were more likely to perform CPR [cardiopulmonary resuscitation]," Drennan said, noting the rate of bystander automated external defibrillator (AED) use was very low in this study. "They also had shorter times for 911-initiated first responders to get to the scene and to the patient."
While this study was intended to compare the rate of survival to hospital discharge for cardiac arrests that occur on higher versus lower floors of residential buildings, it also highlighted the fact that response times for 911-initiated first responders are traditionally measured from the time a call is received by the 911 dispatch center to when the first emergency vehicle arrives on the scene. But Drennan said this measure does not take into account the time required for 911-initiated first responders to reach the patient after they arrive on the scene and can begin resuscitation.
"After collapse from sudden cardiac arrest, early bystander CPR and a shock from a publicly accessible automated external defibrillator can make the difference between life and death," Drennan said. "Effective CPR performed by a bystander immediately after cardiac arrest can more than double a person's chance of survival, but only 30 percent of cardiac arrest victims get CPR from a bystander. With a rapidly deteriorating heart rhythm, in the absence of bystander CPR and defibrillation, cardiac arrests that occurred on higher floors may have a lower probability of survival due to the delay to patient contact by 911-initiated first responders. This early period is essential for bystander interventions by a family member, friend or other willing person to improve survival."
He said another possible explanation for lower survival at higher floors is that it simply takes longer to get patients out of the building.
The study made several recommendations:
- Improving the accessibility of AEDs by placing them on specific floors, in building lobbies, or inside elevators;
- Give paramedics a universal elevator key similar to what firefighters have, giving them sole access to elevators without public interference; and
- Find ways to alert building security to the fact 911-initiated first responders are en route so they can have easy access to the building and elevators waiting on the main floor.
Overall, the study said there was a 20 percent increase in the rate of cardiac arrests suffered in private residences over the years of the study. In roughly the same time period as the study, the number of people living in high-rise building grew by 13 percent in Toronto. Many of those people are older, with higher rates of serious medical issues and higher risk of cardiac arrest.
For more information: www.cmaj.ca


 January 05, 2026
January 05, 2026 









