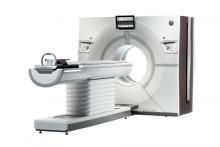
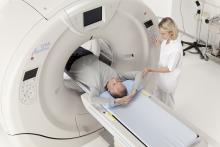
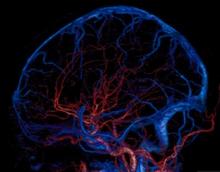
GE Healthcare announced at the Radiological Society of North America Annual Meeting (RSNA 2013) in Chicago that its U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) 510(k)-pending Revolution CT 256-slice system has captured a motion-free image of the human heart in just one beat.
If you enjoy this content, please share it with a colleague
- Read more about GE Healthcare Launches CT Scanner
- Log in or register to post comments