Cardiovascular Systems Inc. announced that it has received U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) clearance for its new ViperWire Advance Peripheral Guide Wire with Flex Tip for their peripheral orbital atherectomy systems (OAS). The new guide wire provides physicians with improved flexibility, navigation and ease-of-use, particularly in hard-to-reach, tortuous vessels when treating arterial calcium associated with peripheral artery disease (PAD).
Heart failure patients had a significantly lower chance of being readmitted within 30 days of discharge when treated with a cardiac resynchronization therapy device (CRT) equipped with an algorithm to automatically deliver and adjust therapy, according to a recent study in JACC: Heart Failure. The study compared these patients to those receiving the standard CRT optimized with echocardiography.
Direct Flow Medical Inc. received Investigational Device Exemption (IDE) approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in April to broaden its SALUS Trial. The expansion includes the addition of high-risk patients and randomization against a commercial device, the Medtronic CoreValve.
Cardiac PET/CT represents a major advancement in cardiovascular diagnostics, offering significant clinical and ...
The Medicines Company announced the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit Court has ruled against the company in its bivalirudin (Angiomax) patent litigation with Hospira Inc.

St. Jude Medical and Thoratec announced that the boards of directors of both companies have unanimously approved a definitive agreement under which St. Jude Medical will acquire all of the outstanding shares of Thoratec. The agreement sets the price for $63.50 per share in a cash transaction valued at approximately $3.4 billion, net of cash acquired.
The recent U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approvals of two next-generation transcatheter aortic valve replacements (TAVR) devices will transform the U.S. market for TAVR procedures over the next decade, according to an analyst with research and consulting firm GlobalData.
SPONSORED CONTENT — Studycast is a comprehensive imaging workflow system that allows healthcare professionals to work ...
Two companion papers published in Academic Emergency Medicine address the question of when it is appropriate to discharge patients experiencing a potentially fatal blood clot. The studies particularly focus on patients presenting with low-risk deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE).
Insulin resistance affects tens of millions of Americans and is a big risk factor for heart disease. Yet, some people with the condition never develop heart disease, while some experience moderate coronary blockages. Others, though, get severe atherosclerosis – multiple blockages and deterioration of coronary arteries characterized by thick, hard, plaque-ridden arterial walls. Researchers at the University of North Carolina (UNC) School of Medicine created a first-of-its-kind animal model to pinpoint two biomarkers that are elevated in the most severe form of coronary disease.
A new study proves race and gender-related disparities exist in care for patients who have recently been diagnosed with atrial fibrillation (AF). The study, published in the July edition of HeartRhythm, the official journal of the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS), includes data from more than 500,000 Medicare beneficiaries. Results notably indicate that female patients compared to male patients are less likely to receive oral anticoagulation, a medication used to lower the likelihood of experiencing a stroke. Women are also less likely than men to receive an ablation, as were Hispanics versus whites.
Providing exceptional cardiovascular care for patients to achieve the best possible outcomes is the number one goal for ...
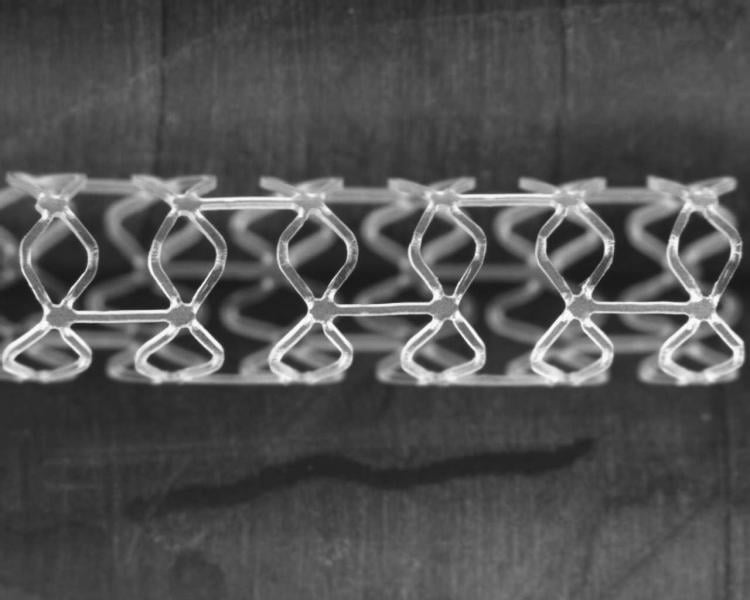
Boston Scientific has initiated a study of the company's first fully resorbable drug-eluting scaffold system. The Fully Absorbable Scaffold Feasibility Study (FAST) is a prospective, single-arm study designed to assess the safety and performance of this next-generation scaffold for the treatment of atherosclerotic coronary lesions.
Veryan Medical announced that the first subject has been enrolled in their MIMICS-2 study at Universitäts-Herzzentrum Freiburg in Bad Krozingen, Germany by the European principal investigator, Prof. Thomas Zeller.

Hospitals in the Midwest were more likely than others to refer patients for guideline-recommended cardiac rehabilitation following angioplasty, according to new original research. This is possibly because more rehab programs are available in the region.
Cardiac positron emission tomography (PET) is growing in popularity among cardiologists because it provides the ability ...

Building teams that include advanced practice providers can help cardiovascular practices meet the challenges of modern practice, according to a new health policy statement by the American College of Cardiology (ACC). These challenges include workforce shortages, an aging patient population with growing complexities in care and a payment system in transition.
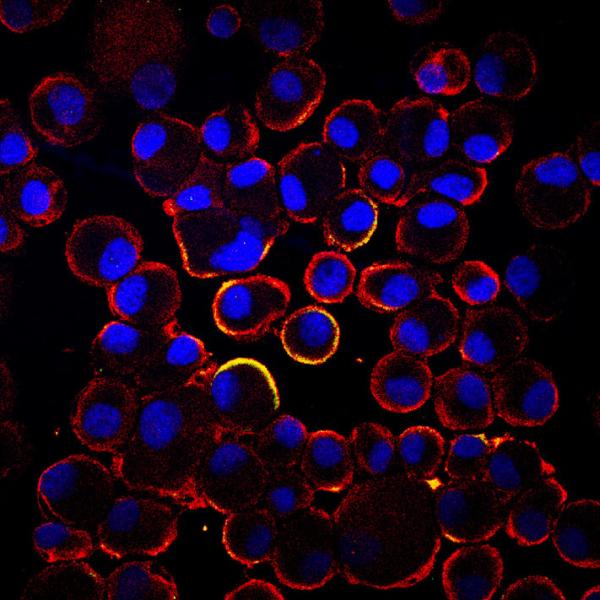
NeoStem Inc. presented updated efficacy and safety results from the one-year follow-up for its Phase 2 PreSERVE study and additional analyses of certain functional tests at the American College of Cardiology’s 64th annual scientific session and expo in March. The one-year follow-up results are defined as all data accumulated until the last patient enrolled completed 12-month follow-up. Thus, the results actually represent data from patients with a median follow-up of 18 months.
Medtronic plc announced the first in-office implant of its miniaturized cardiac monitor as part of the Medtronic Reveal LINQ In-Office 2 (RIO 2) Study. One of the world's smallest cardiac monitors, the Reveal LINQ insertable cardiac monitor (ICM) was successfully implanted in an office setting at Scripps Clinic in La Jolla, California, by cardiologist John Rogers, M.D. The RIO 2 study will determine if the procedure, performed in an in-office setting, is as safe as procedures performed in a traditional hospital setting — such as an operating room, cardiac catheterization laboratory or electrophysiology laboratory.


 July 22, 2015
July 22, 2015