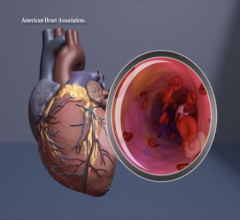
Examples of COVID-19 caused clotting with multiple pulmonary embolisms (PE) in left image, and a large thrombus in the aortic arch. Images courtesy of RSNA and Margarita Revzin et al. Find more clinical images of COVID.
November 23, 2021 — The antiplatelet drug class of P2Y12 inhibitors that block the activity of platelets and prevents clotting, failed to extend survival or lessen disease severity in patients with COVID-19 who were hospitalized but had a relatively moderate case, a new study finds. All patients also received heparin, a commonly used drug that improves outcomes and prevents clots in a different way.[1]
Presented remotely Nov, 15 as a late-breaking study result at the American Heart Association (AHA) Scientific Sessions, the results of the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines-4 (ACTIV-4a) clinical trial show that neither of two protein P2Y12 inhibitors, ticagrelor (Brilinta) or clopidogrel (Plavix), reduced the number of days that patients were alive and free of cardiovascular or respiratory support. Led by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine and the University of Pittsburgh, the study revolves around P2Y12, a protein on the surface of platelets that, upon receiving the right signal, activates them, which makes them “stickier” and more likely to form clots.
Early in the pandemic, abnormal clotting was recognized as a major contributor to COVID-19 severity. The virus is thought to trigger an in rushing of immune cells (inflammation) that damages cells lining blood vessels. This triggers blood platelets to participate in clots, which normally prevent bleeding, but can block blood vessels as part of disease. Mounting evidence suggests that abnormal clotting and related inflammation encourage the tissue death that make the COVID-19 virus deadlier than its relatives that cause the common cold, say the study authors.
“While safe for most patients, P2Y12 inhibitors, when combined with anticoagulation with heparin, neither increased patients’ chances for survival nor reduced the number of days they were free of cardiovascular or respiratory organ support,” says co-corresponding study author Jeffrey S. Berger, M.D., director of the Center for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease at NYU Langone Health and professor in the Departments of Medicine and Surgery at NYU Grossman School of Medicine. “We would have liked to have seen a benefit, but the data nonetheless answer important questions in the field.”
Search Continues for COVID-19 Clotting Treatment
All 562 non-critically ill but hospitalized patients in the current study, whether receiving the P2Y12 inhibitor or not, were treated with heparin, which had been shown in a previous study to increase the chances that patients moderately ill with COVID-19 would avert the need for organ support and be discharged from the hospital. Heparin blocks the action of several proteins (including thrombin) involved in the complex clotting process, and given off by several cell types. Despite this benefit, more than 20 percent of patients with COVID-19 that received heparin in the previous study still died or required intensive care.
Given these limitations, the field has focused on platelet inhibition as one potentially new approach because it had been shown to counter clotting that contributed to blocked coronary arteries and heart attacks. For this reason, patients in the current study were divided into two groups, half randomly chosen to get a P2Y12 inhibitor, and the other half to not receive it, for 14 days or until hospital discharge, whichever came sooner.
The main study measure of treatment effectiveness was organ support–free days, evaluated on a scale that combined in-hospital death and, for those who survived to hospital discharge, the number of days free of cardiovascular or respiratory organ support up to day 21 of hospitalization. The primary safety outcome was bleeding, as platelet inhibitors are known to make it harder for the body to halt bleeding.
Overall, 218 (74 percent) of participants in the P2Y12 inhibitor group and 211 (78 percent) participants in the group that did not get it survived without requiring organ support. Major bleeding occurred in 2 percent of participants randomized to be treated with the P2Y12 inhibitor and in 0.7 percent of those that did not receive the inhibitor.
New Study Arm Will Investigate P-selectin iInhibitor Crizanlizumab to Prevent Clotting in COVID Patients
Moving forward, the ongoing ACTIV-4a trial continues to evaluate P2Y12 inhibitors, not in patients who are moderately ill patients like the current arm, but instead in participants critically ill with COVID-19. Further, two other domains of the ACTIV-4a trial will begin in November 2021, testing the effect of drugs that may reduce clots and improve the function of small blood vessels. One is a P-selectin inhibitor called crizanlizumab in patients hospitalized with COVID-19, says Dr. Berger.
“We are zeroing in on the true damage mechanisms of COVID-19 in blood vessels, and targeting P-selectin and SGLT2 inhibition may block both platelet and endothelial cell activation, and improve the abnormal function of small blood vessels in COVID-19—where P2Y12 inhibitors address only platelets,” says ACTIV-4a study chair Judith S. Hochman, M.D., the Harold Snyder Family Professor of Cardiology, senior associate dean for clinical sciences at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, and a co-corresponding author of the study of moderately ill patients.
The team recently published another study that found, beyond just platelet signals, abnormal crosstalk between blood platelets and cells lining blood vessels (endothelial cells) via P-selectin may be driving abnormal clotting to cause of organ damage in people with severe COVID-19. The other agent is SGLT2 inhibitor, which is a treatment for diabetes and has been shown to improve cardiovascular outcomes in patients without diabetes as well.
“As researchers study mechanisms of severe blood clotting in COVID-19, we’re looking for the ability to target one or more inflammatory pathways to help patients recover faster and avoid severe outcomes,” adds Keith Hoots, M.D., director of the Division of Blood Diseases and Resources at the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI). “The ACTIV Initiative is designed to do just that, quickly, and in way that enables treatments to be nimbly started, scaled, or stopped.”
Along with Dr. Berger and Dr. Hochman, NYU Langone Health study authors were Harmony R. Reynolds, MD, and Erinn M. Hade, PhD. Also authors of the study were Lucy Kornblith of the University of California, San Francisco; Michelle Gong of Albert Einstein College of Medicine; Mary Cushman of the University of Vermont College of Medicine, Burlington; Yu Cheng, Bryan James McVerry, James Luther, and Matthew Neal of the University of Pittsburgh; Keri Kim and John Quigley of University of Illinois at Chicago; Renato Lopes of Duke University Medical Center and Lana Wahid of Duke University Hospital; Bassel Atassi of OSF Little Company of Mary Medical Center; Scott Berry of Berry Consultants; Grant Bochicchio of the Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis; Murillo de Oliveira Antunes of Hospital Universitario Sao Francisco de Assis, São Paulo, Brazil; Michael Farkouh and Patrick Lawler of the Peter Munk Cardiac Centre, Toronto; Yonatan Greenstein of Rutgers New Jersey Medical School; Kristin Hudock and Pooja Khatri of the University of Cincinnati Medical Center; Robert Hyzy of University of Michigan; Andrei Kindzelski of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), Bethesda; Bridget-Anne Kirwan of the Socar Research SA, Nyon, Switzerland; Lisa Baumann Kreuziger of Versiti Blood Research Institute, Milwaukee; Jose Lopez-Sendon Moreno of Hospital Universitario Ramon Y Cajal in Madrid; Jose Lopez-Sendon of Hospital Universitario La Paz, Madrid; Lilia Nigro Maia of Fundação Faculdade Regional De Medicina De São José Do Rio Preto, São José do Rio Preto, Brazil; Robert Sherwin of Wayne State University, Detroit; and Jennifer Wilson of Stanford University Medical Center.
The ACTIV-4a platform was sponsored by the NHLBI, National Institutes of Health (NIH), Bethesda, and administered through OTA-20-011. The research was funded by the NIH Agreement 1OT2HL156812-01. Dr. Berger reports having received consulting fees from Amarin Corporation, Janssen, and Amgen not related to the submitted work. These relationships are being managed in accordance with the policies of NYU Langone.
Find more AHA 2021 late-breaking studies and video
Related COVID Clotting Content:
Overview of Trials for Anticoagulation Therapy for COVID-19 Patients
VIDEO: Antithrombotic Prophylaxis in COVID-19 Patients — Interview with Behnood Bikdeli M.D.
COVID-19 Changes Properties Blood Cells
The Long-term Cardiovascular Impact of COVID-19
Study Supports Early Anticoagulant Treatment to Reduce Death in Moderately Ill COVID-19 Patients
Vascular Disease in COVID-19 is Not Caused by Viral Infection of Blood Vessels
COVID Long-hauler Symptoms May be Caused by Antibody Attacks on ACE2
Prophylaxis Against Venous Thromboembolism in ICU Patients With COVID-19 Using Enoxaparin
COVID-19 Blood Vessel Damage May Cause Brain Fog and Other Long-hauler Symptoms
Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) and the Heart—Is Heart Failure the Next Chapter?
PHOTO GALLERY: How COVID-19 Appears on Medical Imaging (includes images of clotting in various organs)
VIDEO: What Cardiologists Need to Know about COVID-19 — Interview with Thomas Maddox, M.D.
The Cardiac Implications of Novel Coronavirus
Find more cardiology related COVID news
Reference:


 November 14, 2025
November 14, 2025