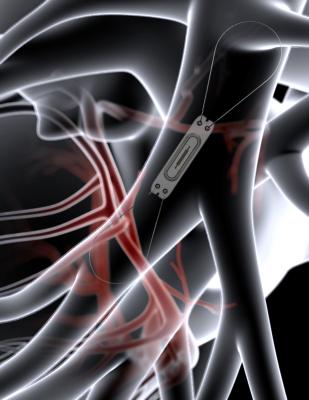
CardioMEMS is a wireless, battery-free sensor that is implanted into the pulmonary artery via a right heart catheterization procedure to transmit pulmonary artery pressures.
September 28, 2021 — Hemodynamic guided management using the CardioMEMS device may reduce heart failure hospitalizations in patients with earlier stage heart failure, according to late-breaking research presented at the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) 2021 Congress and published in The Lancet.[1] The observed reduction did not reach statistical significance in the overall analysis, but was statistically significant when limited to follow-up preceding the COVID-19 pandemic.
In patients with heart failure, pulmonary congestion is a major cause of poor functional capacity, reduced quality of life, heart failure hospitalizations and increased mortality. Elevated or increasing pulmonary artery pressure predicts congestion and can be tracked longitudinally with implantable devices. For most patients with increasing and/or elevated pulmonary artery pressures there is ample time to initiate therapies such as diuretics or vasodilators to reduce pulmonary artery pressure and prevent heart failure hospitalizations.
CardioMEMS is a wireless, battery-free sensor that is implanted into the pulmonary artery via a right heart catheterization procedure to transmit pulmonary artery pressures. Pressure data are used by clinicians to titrate heart failure medications in order to control congestion, optimize pulmonary artery pressures, and prevent heart failure events. The device is approved in Europe and the U.S. to reduce heart failure hospitalizations in patients with New York Heart Association (NYHA) class III heart failure and an admission for heart failure in the previous year.
The GUIDE-HF Trial Randomized Arm examined whether hemodynamic guided heart failure management with the CardioMEMS device reduces heart failure events and mortality in heart failure patients with NYHA class II, III and IV and either a previous heart failure hospitalization or elevated natriuretic peptides.
“The trial was designed to evaluate whether interventions with hemodynamic guided heart failure management provide benefit in earlier (NYHA class II) and later (class IV) stages of heart failure and before a heart failure hospitalization occurs but with biomarkers indicating a potential future risk of heart failure events (i.e. elevated natriuretic peptides),” explained JoAnn Lindenfeld, M.D., of Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville.
The trial enrolled 1,000 patients with NYHA class II–IV heart failure and either a hospitalization for heart failure within the preceding 12 months or elevated natriuretic peptide levels within 30 days prior to consent to participate in the study. All participants underwent implantation of a CardioMEMS device. Patients were then randomized 1:1 to hemodynamic guided management using transmitted pulmonary artery pressure or to a control group that did not have pulmonary artery pressures made available. Patients were blinded to the treatment allocation but the investigators were not blinded.
The primary endpoint was a composite of cumulative heart failure hospitalizations, urgent heart failure visits, and mortality. Heart failure hospitalizations were defined as an inpatient admission for more than 24 hours and an increase in heart failure therapies, primarily intravenous treatments. Urgent heart failure visits were defined as unplanned outpatient visits to a hospital or emergency department for heart failure symptoms requiring intravenous therapy for heart failure.
During a median follow-up of 11.7 months, 253 primary endpoint events occurred in the treatment group and 289 in the control group. In the overall analysis, the primary endpoint was reduced by 12% in the treatment group but did not meet statistical significance (hazard ratio [HR] 0.88; 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.74–1.05; p=0.16). However, a pre-specified COVID-19 impact analysis showed a significant interaction warranting a pre-COVID-19 analysis. The pre-COVID-19 analysis assessed the primary endpoint up to 13 March 2020, the date of the national COVID emergency declaration in the US. The pre-COVID-19 analysis demonstrated a significant 19% reduction in primary endpoint events in the treatment group (HR 0.81; CI 0.66–1.00; p=0.0489).
Regarding heart failure hospitalizations, these were reduced by 17% in the treatment group in the overall analysis but just missed statistical significance (p=0.064). However, the pre-COVID analysis demonstrated a highly significant 28% reduction in heart failure hospitalizations (p=0.0072) – the same reduction achieved in the CHAMPION trial which enrolled NYHA class III heart failure patients with a previous heart failure hospitalization.[2]
Neither urgent heart failure visits nor mortality were reduced independently with treatment in the overall or pre-COVID-19 analyses.
“The findings indicate that the benefits of hemodynamic guided management in reducing heart failure hospitalizations extend to patients with less severe heart failure (NYHA class II) and to those with NYHA II and III symptoms and elevated natriuretic peptides but no previous hospitalization," said Lindenfeld. "The NYHA class IV heart failure patients did not show consistent results but were small in number. The COVID-19 pandemic clearly affected the outcomes of GUIDE-HF, as it did the AFFIRM-AHF trial.[3] Clinical trials conducted during pandemics will require statistical analysis plans to account for their effects.”
Disclosures: Lindenfeld has research grants from AstraZeneca, Volumetrix, Sensible Medical. She is also a consultant for Abbott, Alleviant, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Boston Scientific, CVRx, Edwards Lifesciences, Impulse Dynamics, Medtronic, and V-Wave.
Find more ESC late-breaking studies
Related Heart Failure Technologies to Reduce Hospitalizations:
VIDEO: Remote Heart Failure Monitoring Results in Reduced Readmissions — Interview with William Abraham, M.D.
New CardioMEMS Data Shows Effectiveness in Reducing Heart Failure Readmissions
VIDEO: Technologies to Reduce Heart Failure Readmissions — Interview with William Abraham, M.D.
Abbott Initiates GUIDE-HF Trial for Improved Outcomes With CardioMEMS Monitor
Device Technologies to Reduce Heart Failure Readmissions
Reducing Heart Failure Readmissions
Find more heart failure technology news
References:


 August 29, 2025
August 29, 2025