February 1, 2019 — A team of Rutgers scientists have taken an important step toward the goal of making diseased hearts heal themselves – a new model that would reduce the need for bypass surgery, heart transplants or artificial pumping devices.
The study, recently published in Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology,1 involved removing connective tissue cells from a human heart, reverse-engineering them into heart stem cells, then re-engineering them into heart muscle cells.
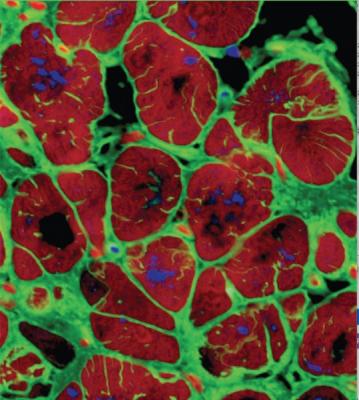
The Rutgers team’s true breakthrough, however, is that the newly created cardiac muscle cells clumped together into a single unit that visibly pumps under the microscope.
Senior author Leonard Y. Lee, chair of the Department of Surgery at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, said cardiac cells made in this way do not normally come together and beat as one. His team succeeded in making this happen by over-expressing, a protein in the cells called CREG.
According to Lee, fibroblasts, a cell in connective tissue, were isolated from the heart tissue and reverse-engineered – or transformed – into stem cells. This was done so that when the CREG protein was over-expressed the stem cells would differentiate into cardiac cells.
“Heart failure has reached epidemic proportions. Right now, the only option to treat it is surgery, transplant or connecting the patient with a blood-pumping machine,” Lee said. “But transplantable hearts are in short supply and mechanical devices limit the patient’s quality of life. So, we are working for ways to help hearts heal themselves.”
Though still far off, Lee’s ultimate goal is to be able to remove small amounts of a patient’s native heart tissue, use CREG to convert the tissue into cardiac muscles that will work together cohesively, and re-introduce them into the patient’s heart allowing it to heal itself.
For more information: www.frontiersin.org/journals/cell-and-developmental-biology
Reference
1. Ghobrial G., Araujo L., Jinwala F., et al. The Structure and Biological Function of CREG. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, Oct. 26, 2018. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2018.00136


 February 03, 2026
February 03, 2026 









